The isolation and characterization of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia T4-like bacteriophage DLP6
- PMID: 28291834
- PMCID: PMC5349666
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0173341
The isolation and characterization of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia T4-like bacteriophage DLP6
Abstract
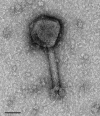
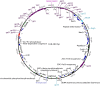
Increasing isolation of the extremely antibiotic resistant bacterium Stenotrophomonas maltophilia has caused alarm worldwide due to the limited treatment options available. A potential treatment option for fighting this bacterium is 'phage therapy', the clinical application of bacteriophages to selectively kill bacteria. Bacteriophage DLP6 (vB_SmoM-DLP6) was isolated from a soil sample using clinical isolate S. maltophilia strain D1571 as host. Host range analysis of phage DLP6 against 27 clinical S. maltophilia isolates shows successful infection and lysis in 13 of the 27 isolates tested. Transmission electron microscopy of DLP6 indicates that it is a member of the Myoviridae family. Complete genome sequencing and analysis of DLP6 reveals its richly recombined evolutionary history, featuring a core of both T4-like and cyanophage genes, which suggests that it is a member of the T4-superfamily. Unlike other T4-superfamily phages however, DLP6 features a transposase and ends with 229 bp direct terminal repeats. The isolation of this bacteriophage is an exciting discovery due to the divergent nature of DLP6 in relation to the T4-superfamily of phages.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization. Antimicrobial resistance: global report on surveillance. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2014.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

