Reproducibility of patient setup in the seated treatment position: A novel treatment chair design
- PMID: 28291911
- PMCID: PMC5689874
- DOI: 10.1002/acm2.12024
Reproducibility of patient setup in the seated treatment position: A novel treatment chair design
Abstract
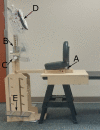
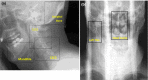
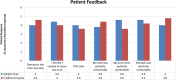
Radiotherapy in a seated position may be indicated for patients who are unable to lie on the treatment couch for the duration of treatment, in scenarios where a seated treatment position provides superior anatomical positioning and dose distributions, or for a low-cost system designed using a fixed treatment beam and rotating seated patient. In this study, we report a novel treatment chair that was constructed to allow for three-dimensional imaging and treatment delivery while ensuring robust immobilization, providing reproducibility equivalent to that in the traditional supine position. Five patients undergoing radiation treatment for head-and-neck cancers were enrolled and were setup in the chair, with immobilization devices created, and then imaged with orthogonal X-rays in a scenario that mimicked radiation treatments (without treatment delivery). Six subregions of the acquired images were rigidly registered to evaluate intra- and interfraction displacement and chair construction. Displacements under conditions of simulated image guidance were acquired by first registering one subregion; the residual displacement of other subregions was then measured. Additionally, we administered a patient questionnaire to gain patient feedback and assess comparison to the supine position. Average inter- and intrafraction displacements of all subregions in the seated position were less than 2 and 3 mm, respectively. When image guidance was simulated, L-R and A-P interfraction displacements were reduced by an average of 1 mm, providing setup of comparable quality to supine setups. The enrolled patients, who had no indication for a seated treatment position, reported no preference in the seated or the supine position. The novel chair design provides acceptable inter- and intrafraction displacement, with reproducibility equivalent to that reported for patients in the supine position. Patient feedback will be incorporated in the refinement of the chair, facilitating treatment of head-and-neck cancer in patients who are unable to lie for the duration of treatment or for use in an economical fixed-beam setup.
Keywords: novel treatment positioning; patient positioning; upright treatment.
© 2017 The Authors. Journal of Applied Clinical Medical Physics published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of American Association of Physicists in Medicine.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Minimal mask immobilization with optical surface guidance for head and neck radiotherapy.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2018 Jan;19(1):17-24. doi: 10.1002/acm2.12211. Epub 2017 Nov 9. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2018. PMID: 29119677 Free PMC article.
-
Improved setup and positioning accuracy using a three-point customized cushion/mask/bite-block immobilization system for stereotactic reirradiation of head and neck cancer.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2016 May 8;17(3):180-189. doi: 10.1120/jacmp.v17i3.6038. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2016. PMID: 27167275 Free PMC article.
-
Immobilisation accuracy of double shell positioning system for stereotactic radiotherapy in patients with brain tumors.J Med Imaging Radiat Sci. 2025 Mar;56(2):101817. doi: 10.1016/j.jmir.2024.101817. Epub 2024 Dec 13. J Med Imaging Radiat Sci. 2025. PMID: 39673831
-
Adaptive radiotherapy of head and neck cancer.Semin Radiat Oncol. 2010 Apr;20(2):84-93. doi: 10.1016/j.semradonc.2009.11.002. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2010. PMID: 20219546 Review.
-
Dynamic targeting image-guided radiotherapy.Med Dosim. 2006 Summer;31(2):113-25. doi: 10.1016/j.meddos.2005.12.014. Med Dosim. 2006. PMID: 16690452 Review.
Cited by
-
Biological and Mechanical Synergies to Deal With Proton Therapy Pitfalls: Minibeams, FLASH, Arcs, and Gantryless Rooms.Front Oncol. 2021 Jan 21;10:613669. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.613669. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33585238 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical Implementation of a 6D Treatment Chair for Fixed Ion Beam Lines.Front Oncol. 2021 Jun 23;11:694749. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.694749. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34249751 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analysis of residual setup errors in head and neck patients from upright versus supine radiotherapy postures.Med Phys. 2025 Jul;52(7):e17824. doi: 10.1002/mp.17824. Epub 2025 Apr 11. Med Phys. 2025. PMID: 40216595 Free PMC article.
-
Upright patient positioning for gantry-free breast radiotherapy: feasibility tests using a robotic chair and specialised bras.Front Oncol. 2023 Sep 22;13:1250678. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1250678. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37810987 Free PMC article.
-
Upright patient positioning for pelvic radiotherapy treatments.Tech Innov Patient Support Radiat Oncol. 2022 Nov 28;24:124-130. doi: 10.1016/j.tipsro.2022.11.003. eCollection 2022 Dec. Tech Innov Patient Support Radiat Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36471684 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yang J, Chu D, Dong L, Court LE. Advantages of simulating thoracic cancer patients in an upright position. Pract Radiat Oncol. 2014;4:e53–e58. - PubMed
-
- Dellamonica J, Lerolle N, Sargentini C, et al. Effect of different seated positions on lung volume and oxygenation in acute respiratory distress syndrome. Intensive Care Med. 2013;39:1121–1127. - PubMed
-
- Graham MV, Purdy JA, Emami B, et al. Clinical dose–volume histogram analysis for pneumonitis after 3D treatment for non‐small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1999;45:323–329. - PubMed
-
- Hsieh M, Balter P, Beadle B, Chi P, Stingo F, Court L. SU‐E‐T‐273: radiation shielding for a fixed horizontal‐beam linac in a shipping container and a conventional treatment vault. Med Phys. 2014;41:286.
-
- Court L, Yang J, Fullen D, et al. SU‐E‐T‐359: patients could (and should) be treated in an upright position. Med Phys. 2013;40:287.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

