Room scatter effects in Total Skin Electron Irradiation: Monte Carlo simulation study
- PMID: 28291915
- PMCID: PMC5689893
- DOI: 10.1002/acm2.12039
Room scatter effects in Total Skin Electron Irradiation: Monte Carlo simulation study
Abstract
Purpose: Total Skin Electron Irradiation (TSEI) is a complex technique which usually involves the use of large electron fields and the dual-field approach. In this situation, many electrons scattered from the treatment room floor are produced. However, no investigations of the effect of scattered electrons in TSEI treatments have been reported. The purpose of this work was to study the contribution of floor scattered electrons to skin dose during TSEI treatment using Monte Carlo (MC) simulations.
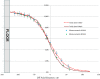
Methods: All MC simulations were performed with the EGSnrc code. Influence of beam energy, dual-field angle, and floor material on the contribution of floor scatter was investigated. Spectrum of the scattered electrons was calculated. Measurements of dose profile were performed in order to verify MC calculations.
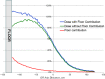
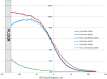
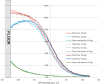
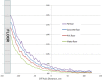
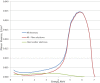
Results: Floor scatter dependency on the floor material was observed (at 20 cm from the floor, scatter contribution was about 21%, 18%, 15%, and 12% for iron, concrete, PVC, and water, respectively). Although total dose profiles exhibited slight variation as functions of beam energy and dual-field angle, no dependence of the floor scatter contribution on the beam energy or dual-field angle was found. The spectrum of the scattered electrons was almost uniform between a few hundred KeV to 4 MeV, and then decreased linearly to 6 MeV.
Conclusions: For the TSEI technique, dose contribution due to the electrons scattered from the room floor may be clinically significant and should be taken into account during design and commissioning phases. MC calculations can be used for this task.
Keywords: Monte Carlo simulation; Total Skin Electron Irradiation; dosimetry.
© 2017 The Authors. Journal of Applied Clinical Medical Physics published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of American Association of Physicists in Medicine.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Validation of total skin electron irradiation (TSEI) technique dosimetry data by Monte Carlo simulation.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2016 Jul 8;17(4):418-429. doi: 10.1120/jacmp.v17i4.6230. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2016. PMID: 27455502 Free PMC article.
-
Monte Carlo techniques for scattering foil design and dosimetry in total skin electron irradiations.Med Phys. 2005 Jun;32(6):1460-8. doi: 10.1118/1.1924368. Med Phys. 2005. PMID: 16013701
-
Improving treatment geometries in total skin electron therapy: Experimental investigation of linac angles and floor scatter dose contributions using Cherenkov imaging.Med Phys. 2018 Jun;45(6):2639-2646. doi: 10.1002/mp.12917. Epub 2018 May 6. Med Phys. 2018. PMID: 29663425
-
High-density dental implants and radiotherapy planning: evaluation of effects on dose distribution using pencil beam convolution algorithm and Monte Carlo method.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2015 Sep 8;16(5):46–52. doi: 10.1120/jacmp.v16i5.5612. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2015. PMID: 26699323 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modeling scatter through sides of island blocks used for intensity-modulated bolus electron conformal therapy.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2023 Feb;24(2):e13889. doi: 10.1002/acm2.13889. Epub 2023 Jan 7. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2023. PMID: 36610042 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Validation of the dosimetry of total skin irradiation techniques by Monte Carlo simulation.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2020 Aug;21(8):107-119. doi: 10.1002/acm2.12921. Epub 2020 Jun 19. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2020. PMID: 32559022 Free PMC article.
-
Electron beam irradiation on novel coronavirus (COVID-19): A Monte-Carlo simulation.Chin Phys B. 2020 Apr;29(4):048703. doi: 10.1088/1674-1056/ab7dac. Chin Phys B. 2020. PMID: 34191933 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of effect of filter on the stand-up technique for total skin irradiation by Monte Carlo simulation.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2021 Jan;22(1):137-145. doi: 10.1002/acm2.13119. Epub 2020 Dec 12. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2021. PMID: 33314659 Free PMC article.
-
Dosimetry, Optimization and FMEA of Total Skin Electron Irradiation (TSEI).Z Med Phys. 2022 May;32(2):228-239. doi: 10.1016/j.zemedi.2021.09.004. Epub 2021 Nov 2. Z Med Phys. 2022. PMID: 34740500 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Desai KR, Pezner RD, Lipsett JA, et al. Total skin electron irradiation for mycosis fungoides: relationship between acute toxicities and measured dose at different anatomic sites. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1988;15:641–645. - PubMed
-
- Diamantopoulos S, Platoni K, Dilvoi M, et al. Clinical implementation of total skin electron beam (TSEB) therapy: a review of the relevant literature. Phys Med. 2011;27:62–68. doi:10.1016/j.ejmp.2010.09.001. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Piotrowski T, Milecki P, Skorska M, Fundowicz D. Total skin electron irradiation techniques: a review. Postepy Derm Alergol. 2013;30:50–55. doi:10.5114/pdia.2013.33379. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jones G, Wilson LD, Fox‐Goguen L. Total skin electron beam radiotherapy for patients who have mycosis fungoides. Hematol Oncol Clin N Am. 2003;17:1421–1434. - PubMed
-
- Anacak Y, Arican Z, Bar‐Deroma R, Tamir A, Kuten A. Total skin electron irradiation: evaluation of dose uniformity throughout the skin surface. Med Dosim. 2003;28:31–34. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

