Arabidopsis MAP3K16 and Other Salt-Inducible MAP3Ks Regulate ABA Response Redundantly
- PMID: 28292003
- PMCID: PMC5386961
- DOI: 10.14348/molcells.2017.0002
Arabidopsis MAP3K16 and Other Salt-Inducible MAP3Ks Regulate ABA Response Redundantly
Abstract
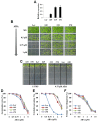
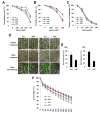
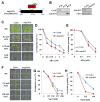
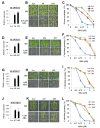
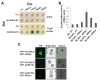
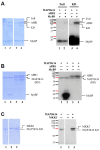
In the Arabidopsis genome, approximately 80 MAP3Ks (mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinases) have been identified. However, only a few of them have been characterized, and the functions of most MAP3Ks are largely unknown. In this paper, we report the function of MAP3K16 and several other MAP3Ks, MAP3K14/15/17/18, whose expression is salt-inducible. We prepared MAP3K16 overexpression (OX) lines and analyzed their phenotypes. The result showed that the transgenic plants were ABA-insensitive during seed germination and cotyledon greening stage but their root growth was ABA-hypersensitive. The OX lines were more susceptible to water-deficit condition at later growth stage in soil. A MAP3K16 knockout (KO) line, on the other hand, exhibited opposite phenotypes. In similar transgenic analyses, we found that MAP3K14/15/17/18 OX and KO lines displayed similar phenotypes to those of MA3K16, suggesting the functional redundancy among them. MAP3K16 possesses in vitro kinase activity, and we carried out two-hybrid analyses to identify MAP3K16 substrates. Our results indicate that MAP3K16 interacts with MKK3 and the negative regulator of ABA response, ABR1, in yeast. Furthermore, MAP3K16 recombinant protein could phosphorylate MKK3 and ABR1, suggesting that they might be MAP3K16 substrates. Collectively, our results demonstrate that MAP3K16 and MAP3K14/15/17/18 are involved in ABA response, playing negative or positive roles depending on developmental stage and that MAP3K16 may function via MKK3 and ABR1.
Keywords: Arabidopsis thaliana; MAP kinase; MAP3K16; abiotic stress; abscisic acid (ABA).
Figures


Similar articles
-
Arabidopsis putative MAP kinase kinase kinases Raf10 and Raf11 are positive regulators of seed dormancy and ABA response.Plant Cell Physiol. 2015 Jan;56(1):84-97. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcu148. Epub 2014 Oct 15. Plant Cell Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25324504
-
Overexpression of HbMBF1a, encoding multiprotein bridging factor 1 from the halophyte Hordeum brevisubulatum, confers salinity tolerance and ABA insensitivity to transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana.Plant Mol Biol. 2020 Jan;102(1-2):1-17. doi: 10.1007/s11103-019-00926-7. Epub 2019 Oct 26. Plant Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 31655970 Free PMC article.
-
An abscisic acid inducible Arabidopsis MAPKKK, MAPKKK18 regulates leaf senescence via its kinase activity.Plant Mol Biol. 2015 Apr;87(6):565-75. doi: 10.1007/s11103-015-0295-0. Epub 2015 Feb 14. Plant Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25680457
-
Updates on the Role of ABSCISIC ACID INSENSITIVE 5 (ABI5) and ABSCISIC ACID-RESPONSIVE ELEMENT BINDING FACTORs (ABFs) in ABA Signaling in Different Developmental Stages in Plants.Cells. 2021 Aug 5;10(8):1996. doi: 10.3390/cells10081996. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34440762 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From growth to stress: RAF-like kinases as integrators of hormonal signals in plants.J Exp Bot. 2025 May 10;76(7):1978-1986. doi: 10.1093/jxb/eraf086. J Exp Bot. 2025. PMID: 40096526 Review.
Cited by
-
StMAPKK5 responds to heat stress by regulating potato growth, photosynthesis, and antioxidant defenses.Front Plant Sci. 2024 May 16;15:1392425. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1392425. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 38817936 Free PMC article.
-
MKK3 Cascade Regulates Seed Dormancy Through a Negative Feedback Loop Modulating ABA Signal in Rice.Rice (N Y). 2024 Jan 3;17(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s12284-023-00679-4. Rice (N Y). 2024. PMID: 38170405 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring Breakthroughs in Three Traits Belonging to Seed Life.Plants (Basel). 2022 Feb 11;11(4):490. doi: 10.3390/plants11040490. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35214823 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The MKKK62-MKK3-MAPK7/14 module negatively regulates seed dormancy in rice.Rice (N Y). 2019 Jan 22;12(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s12284-018-0260-z. Rice (N Y). 2019. PMID: 30671680 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic profiling of wheat near-isogenic lines reveals candidate genes on chromosome 3A for pre-harvest sprouting resistance.BMC Plant Biol. 2021 Jan 21;21(1):53. doi: 10.1186/s12870-021-02824-x. BMC Plant Biol. 2021. PMID: 33478384 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Asai T., Tena G., Plotnikova J., Willmann M.R., Chiu W.L., Gomez-Gomez L., Boller T., Ausubel F.M., Sheen J. MAP kinase signalling cascade in Arabidopsis innate immunity. Nature. 2002;415:977–983. - PubMed
-
- Bechtold N., Pelletier G. In planta Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of adult Arabidopsis thaliana plants by vacuum infiltration. Methods in Mol Biol. 1998;82:259–266. - PubMed
-
- Choi H., Hong J., Ha J., Kang J., Kim S.Y. ABFs, a family of ABA-responsive element binding factors. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:1723–1730. - PubMed
-
- Choi H.I., Park H.J., Park J.H., Kim S., Im M.Y., Seo H.H., Kim Y.W., Hwang I., Kim S.Y. Arabidopsis calcium-dependent protein kinase AtCPK32 interacts with ABF4, a transcriptional regulator of abscisic acid-responsive gene expression, and modulates its activity. Plant Physiol. 2005;139:1750–1761. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Colcombet J., Hirt H. Arabidopsis MAPKs: a complex signalling network involved in multiple biological processes. Biochem J. 2008;413:217–226. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

