Production of BP178, a derivative of the synthetic antibacterial peptide BP100, in the rice seed endosperm
- PMID: 28292258
- PMCID: PMC5351061
- DOI: 10.1186/s12870-017-1011-9
Production of BP178, a derivative of the synthetic antibacterial peptide BP100, in the rice seed endosperm
Abstract
Background: BP178 peptide is a synthetic BP100-magainin derivative possessing strong inhibitory activity against plant pathogenic bacteria, offering a great potential for future applications in plant protection and other fields. Here we report the production and recovery of a bioactive BP178 peptide using rice seeds as biofactories.
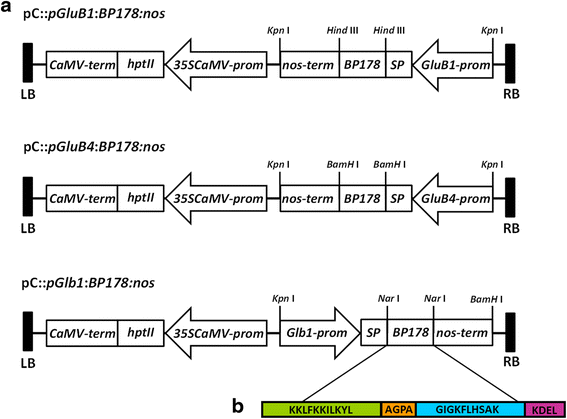
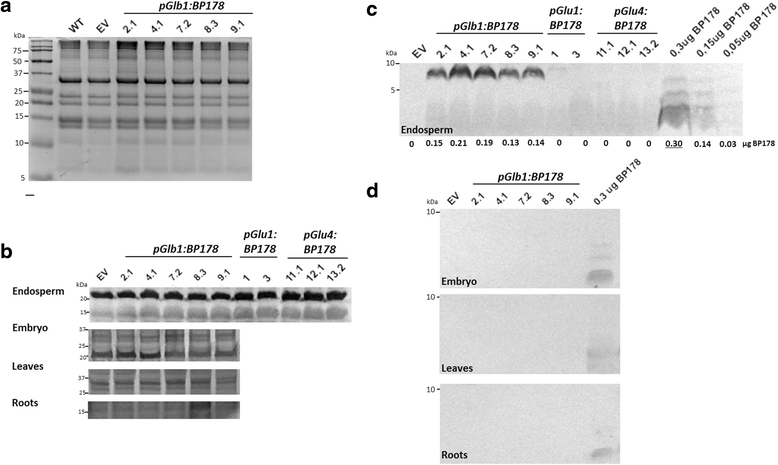
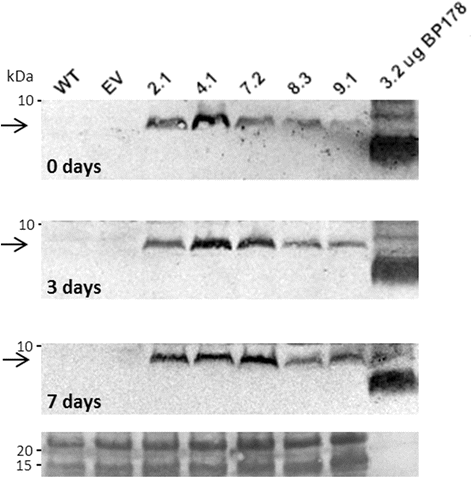
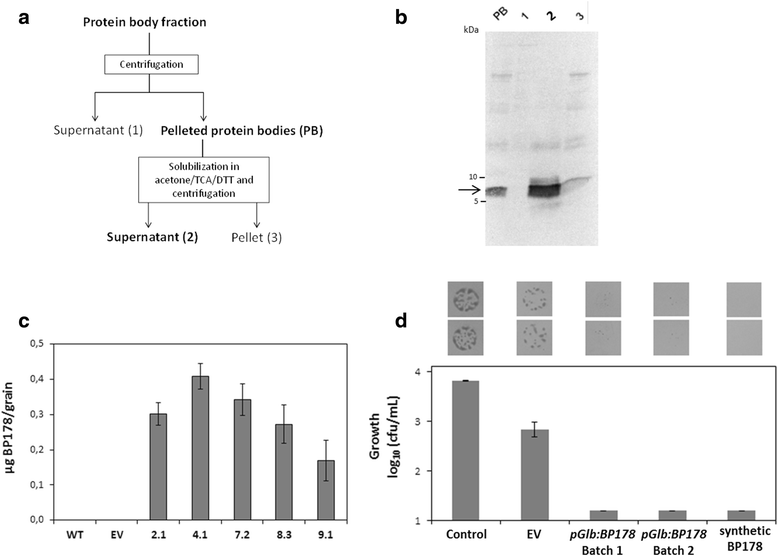
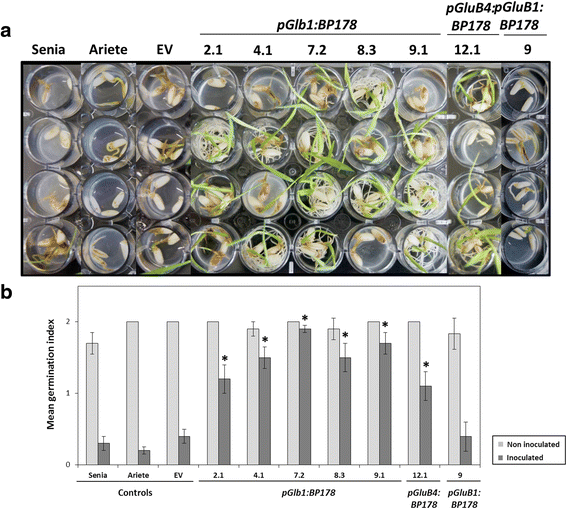
Results: A synthetic gene encoding the BP178 peptide was prepared and introduced in rice plants. The gene was efficiently expressed in transgenic rice under the control of an endosperm-specific promoter. Among the three endosperm-specific rice promoters (Glutelin B1, Glutelin B4 or Globulin 1), best results were obtained when using the Globulin 1 promoter. The BP178 peptide accumulated in the seed endosperm and was easily recovered from rice seeds using a simple procedure with a yield of 21 μg/g. The transgene was stably inherited for at least three generations, and peptide accumulation remained stable during long term storage of transgenic seeds. The purified peptide showed in vitro activity against the bacterial plant pathogen Dickeya sp., the causal agent of the dark brown sheath rot of rice. Seedlings of transgenic events showed enhanced resistance to the fungal pathogen Fusarium verticillioides, supporting that the in planta produced peptide was biologically active.
Conclusions: The strategy developed in this work for the sustainable production of BP178 peptide using rice seeds as biofactories represents a promising system for future production of peptides for plant protection and possibly in other fields.
Keywords: Antimicrobial peptide; Oryza sativa; Pathogen resistance; Peptide recovery; Protein bodies; Rice biofactory.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

