Sex differences in gout characteristics: tailoring care for women and men
- PMID: 28292303
- PMCID: PMC5351188
- DOI: 10.1186/s12891-017-1465-9
Sex differences in gout characteristics: tailoring care for women and men
Abstract
Background: To characterize the differences between women and men with gout.
Methods: We analyzed a US national cohort of gout patients cared for by rheumatologists.
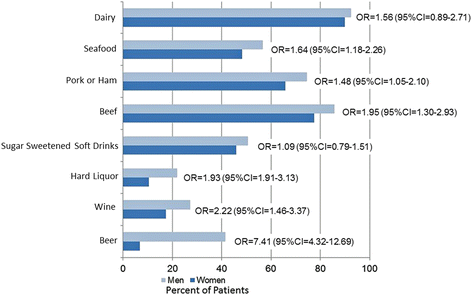
Results: Compared with the 1012 men with gout, women with gout (n = 262) were older (71 vs. 61 years, p < 0.001) and had a greater burden of comorbid conditions (p < 0.001 for hypertension, diabetes, renal disease and obesity). Risk factors for gout differed with women more often taking diuretics (p < 0.001), while men more frequently had dietary triggers (p < 0.05).
Conclusions: The profiles of women and men with gout are markedly different, suggesting a need to tailor treatment recommendations.
Keywords: Comorbidity; Gender; Gout; Quality of Care.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical