Synonymous Codons: Choose Wisely for Expression
- PMID: 28292534
- PMCID: PMC5409834
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tig.2017.02.001
Synonymous Codons: Choose Wisely for Expression
Abstract
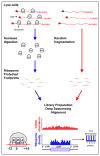
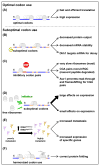
The genetic code, which defines the amino acid sequence of a protein, also contains information that influences the rate and efficiency of translation. Neither the mechanisms nor functions of codon-mediated regulation were well understood. The prevailing model was that the slow translation of codons decoded by rare tRNAs reduces efficiency. Recent genome-wide analyses have clarified several issues. Specific codons and codon combinations modulate ribosome speed and facilitate protein folding. However, tRNA availability is not the sole determinant of rate; rather, interactions between adjacent codons and wobble base pairing are key. One mechanism linking translation efficiency and codon use is that slower decoding is coupled to reduced mRNA stability. Changes in tRNA supply mediate biological regulationfor instance,, changes in tRNA amounts facilitate cancer metastasis.
Keywords: codon pair; mRNA decay; protein folding; ribosome profiling; synonymous codons; translation.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- de Godoy LM, et al. Comprehensive mass-spectrometry-based proteome quantification of haploid versus diploid yeast. Nature. 2008;455:1251–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

