Cell membrane-derived nanomaterials for biomedical applications
- PMID: 28292726
- PMCID: PMC5417338
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2017.02.041
Cell membrane-derived nanomaterials for biomedical applications
Abstract
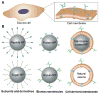
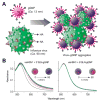
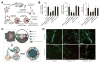
The continued evolution of biomedical nanotechnology has enabled clinicians to better detect, prevent, manage, and treat human disease. In order to further push the limits of nanoparticle performance and functionality, there has recently been a paradigm shift towards biomimetic design strategies. By taking inspiration from nature, the goal is to create next-generation nanoparticle platforms that can more effectively navigate and interact with the incredibly complex biological systems that exist within the body. Of great interest are cellular membranes, which play essential roles in biointerfacing, self-identification, signal transduction, and compartmentalization. In this review, we explore the major ways in which researchers have directly leveraged cell membrane-derived biomaterials for the fabrication of novel nanotherapeutics and nanodiagnostics. Such emerging technologies have the potential to significantly advance the field of nanomedicine, helping to improve upon traditional modalities while also enabling novel applications.
Keywords: Biomimetic nanoparticle; Cell membrane; Detoxification; Drug delivery; Imaging; Immunotherapy.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

