Writing for Health: Rationale and Protocol for a Randomized Controlled Trial of Internet-Based Benefit-Finding Writing for Adults With Type 1 or Type 2 Diabetes
- PMID: 28292741
- PMCID: PMC5373675
- DOI: 10.2196/resprot.7151
Writing for Health: Rationale and Protocol for a Randomized Controlled Trial of Internet-Based Benefit-Finding Writing for Adults With Type 1 or Type 2 Diabetes
Abstract
Background: Diabetes mellitus is Australia's fastest growing chronic disease, and has high comorbidity with depression. Both subthreshold depression and diabetes distress are common amongst people with type 1 or type 2 diabetes, and are associated with poorer diabetes self-care. A need exists for low-intensity self-help interventions for large numbers of people with diabetes and diabetes distress or subthreshold depression, as part of a stepped-care approach to meeting the psychological needs of people with diabetes. Benefit-finding writing is a very brief intervention that involves writing about any positive thoughts and feelings about a stressful experience, such as an illness. Benefit-finding writing has been associated with increases in positive affect and positive growth, and has demonstrated promising results in trials amongst other clinical populations. However, benefit-finding writing has not yet been examined in people with diabetes.
Objective: The aim of this randomized controlled trial (RCT) is to evaluate the efficacy of an Internet-based benefit-finding writing (iBFW) intervention for adults with type 1 or type 2 diabetes (compared to a control writing condition) for reducing diabetes distress and increasing benefit-finding in diabetes, and also improving a range of secondary outcomes.
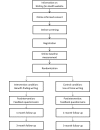
Methods: A two-arm RCT will be conducted, using the online program Writing for Health. Adults with type 1 or type 2 diabetes living in Australia will be recruited using diabetes-related publications and websites, and through advertisements in diabetes services and general practitioners' offices. Potential participants will be referred to the study-specific website for participant information and screening. All data will be collected online. Participants will be randomized to either iBFW about diabetes, or a control writing condition of writing about use-of-time. Both conditions involve three daily sessions (once per day for three consecutive days) of 15-minute online writing exercises. Outcome measures will be administered online at baseline, one-month, and three-month follow-ups.
Results: This trial is currently underway. The primary outcomes will be diabetes distress and benefit-finding in diabetes. Secondary outcomes will be depression, anxiety, diabetes self-care, perceived health, and health care utilization. We aim to recruit 104 participants. All stages of the study will be conducted online using the Writing for Health program. Group differences will be analyzed on an intention-to-treat basis using mixed models repeated measures. Linguistic analyses of the writing exercise scripts, and examinations of the immediate emotional responses to the writing exercises, will also be undertaken.
Conclusions: This RCT will be the first study to examine iBFW for adults with type 1 or type 2 diabetes. If iBFW is found to be efficacious in reducing diabetes distress and improving diabetes self-care and other outcomes, iBFW may offer the potential to be a low-cost, easily accessible self-help intervention to improve the wellbeing of adults with diabetes.
Trial registration: Australia and New Zealand Clinical Trials Registry (ACTRN12615000241538).
Keywords: Internet intervention; diabetes-related distress; randomized controlled trial; type 1 diabetes; type 2 diabetes; writing.
©Joanna Crawford, Kay Wilhelm, Lisa Robins, Judy Proudfoot. Originally published in JMIR Research Protocols (http://www.researchprotocols.org), 14.03.2017.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Murray CJ, Vos T, Lozano R, Naghavi M, Flaxman AD, Michaud C, Ezzati M, Shibuya K, Salomon JA, Abdalla S, Aboyans V, Abraham J, Ackerman I, Aggarwal R, Ahn SY, Ali MK, Alvarado M, Anderson HR, Anderson LM, Andrews KG, Atkinson C, Baddour LM, Bahalim AN, Barker-Collo S, Barrero LH, Bartels DH, Basáñez MG, Baxter A, Bell ML, Benjamin EJ, Bennett D, Bernabé E, Bhalla K, Bhandari B, Bikbov B, Bin AA, Birbeck G, Black JA, Blencowe H, Blore JD, Blyth F, Bolliger I, Bonaventure A, Boufous S, Bourne R, Boussinesq M, Braithwaite T, Brayne C, Bridgett L, Brooker S, Brooks P, Brugha TS, Bryan-Hancock C, Bucello C, Buchbinder R, Buckle G, Budke CM, Burch M, Burney P, Burstein R, Calabria B, Campbell B, Canter CE, Carabin H, Carapetis J, Carmona L, Cella C, Charlson F, Chen H, Cheng AT, Chou D, Chugh SS, Coffeng LE, Colan SD, Colquhoun S, Colson KE, Condon J, Connor MD, Cooper LT, Corriere M, Cortinovis M, de Vaccaro KC, Couser W, Cowie BC, Criqui MH, Cross M, Dabhadkar KC, Dahiya M, Dahodwala N, Damsere-Derry J, Danaei G, Davis A, De Leo D, Degenhardt L, Dellavalle R, Delossantos A, Denenberg J, Derrett S, Des Jarlais DC, Dharmaratne SD, Dherani M, Diaz-Torne C, Dolk H, Dorsey ER, Driscoll T, Duber H, Ebel B, Edmond K, Elbaz A, Ali SE, Erskine H, Erwin PJ, Espindola P, Ewoigbokhan SE, Farzadfar F, Feigin V, Felson DT, Ferrari A, Ferri CP, Fèvre EM, Finucane MM, Flaxman S, Flood L, Foreman K, Forouzanfar MH, Fowkes FG, Fransen M, Freeman MK, Gabbe BJ, Gabriel SE, Gakidou E, Ganatra HA, Garcia B, Gaspari F, Gillum RF, Gmel G, Gonzalez-Medina D, Gosselin R, Grainger R, Grant B, Groeger J, Guillemin F, Gunnell D, Gupta R, Haagsma J, Hagan H, Halasa YA, Hall W, Haring D, Haro JM, Harrison JE, Havmoeller R, Hay RJ, Higashi H, Hill C, Hoen B, Hoffman H, Hotez PJ, Hoy D, Huang JJ, Ibeanusi SE, Jacobsen KH, James SL, Jarvis D, Jasrasaria R, Jayaraman S, Johns N, Jonas JB, Karthikeyan G, Kassebaum N, Kawakami N, Keren A, Khoo J, King CH, Knowlton LM, Kobusingye O, Koranteng A, Krishnamurthi R, Laden F, Lalloo R, Laslett LL, Lathlean T, Leasher JL, Lee YY, Leigh J, Levinson D, Lim SS, Limb E, Lin JK, Lipnick M, Lipshultz SE, Liu W, Loane M, Ohno SL, Lyons R, Mabweijano J, MacIntyre MF, Malekzadeh R, Mallinger L, Manivannan S, Marcenes W, March L, Margolis DJ, Marks GB, Marks R, Matsumori A, Matzopoulos R, Mayosi BM, McAnulty JH, McDermott MM, McGill N, McGrath J, Medina-Mora ME, Meltzer M, Mensah GA, Merriman TR, Meyer A, Miglioli V, Miller M, Miller TR, Mitchell PB, Mock C, Mocumbi AO, Moffitt TE, Mokdad AA, Monasta L, Montico M, Moradi-Lakeh M, Moran A, Morawska L, Mori R, Murdoch ME, Mwaniki MK, Naidoo K, Nair MN, Naldi L, Narayan KM, Nelson PK, Nelson RG, Nevitt MC, Newton CR, Nolte S, Norman P, Norman R, O'Donnell M, O'Hanlon S, Olives C, Omer SB, Ortblad K, Osborne R, Ozgediz D, Page A, Pahari B, Pandian JD, Rivero AP, Patten SB, Pearce N, Padilla RP, Perez-Ruiz F, Perico N, Pesudovs K, Phillips D, Phillips MR, Pierce K, Pion S, Polanczyk GV, Polinder S, Pope CA, Popova S, Porrini E, Pourmalek F, Prince M, Pullan RL, Ramaiah KD, Ranganathan D, Razavi H, Regan M, Rehm JT, Rein DB, Remuzzi G, Richardson K, Rivara FP, Roberts T, Robinson C, De Leòn FR, Ronfani L, Room R, Rosenfeld LC, Rushton L, Sacco RL, Saha S, Sampson U, Sanchez-Riera L, Sanman E, Schwebel DC, Scott JG, Segui-Gomez M, Shahraz S, Shepard DS, Shin H, Shivakoti R, Singh D, Singh GM, Singh JA, Singleton J, Sleet DA, Sliwa K, Smith E, Smith JL, Stapelberg NJ, Steer A, Steiner T, Stolk WA, Stovner LJ, Sudfeld C, Syed S, Tamburlini G, Tavakkoli M, Taylor HR, Taylor JA, Taylor WJ, Thomas B, Thomson WM, Thurston GD, Tleyjeh IM, Tonelli M, Towbin JA, Truelsen T, Tsilimbaris MK, Ubeda C, Undurraga EA, van der Werf MJ, van OS J, Vavilala MS, Venketasubramanian N, Wang M, Wang W, Watt K, Weatherall DJ, Weinstock MA, Weintraub R, Weisskopf MG, Weissman MM, White RA, Whiteford H, Wiebe N, Wiersma ST, Wilkinson JD, Williams HC, Williams SR, Witt E, Wolfe F, Woolf AD, Wulf S, Yeh P, Zaidi AK, Zheng Z, Zonies D, Lopez AD, AlMazroa MA, Memish ZA. Disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) for 291 diseases and injuries in 21 regions, 1990-2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 2012 Dec 15;380(9859):2197–223. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61689-4.S0140-6736(12)61689-4 - DOI - PubMed
-
- NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC) Worldwide trends in diabetes since 1980: a pooled analysis of 751 population-based studies with 4.4 million participants. Lancet. 2016 Apr 09;387(10027):1513–30. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)00618-8. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0140-6736(16)00618-8 S0140-6736(16)00618-8 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Anderson RJ, Freedland KE, Clouse RE, Lustman PJ. The prevalence of comorbid depression in adults with diabetes: a meta-analysis. Diabetes Care. 2001 Jun;24(6):1069–78. - PubMed
-
- Grigsby AB, Anderson RJ, Freedland KE, Clouse RE, Lustman PJ. Prevalence of anxiety in adults with diabetes: a systematic review. J Psychosom Res. 2002 Dec;53(6):1053–60.S0022399902004178 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical