Using brain organoids to understand Zika virus-induced microcephaly
- PMID: 28292840
- PMCID: PMC5358105
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.140707
Using brain organoids to understand Zika virus-induced microcephaly
Abstract
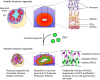
Technologies to differentiate human pluripotent stem cells into three-dimensional organized structures that resemble in vivo organs are pushing the frontiers of human disease modeling and drug development. In response to the global health emergency posed by the Zika virus (ZIKV) outbreak, brain organoids engineered to mimic the developing human fetal brain have been employed to model ZIKV-induced microcephaly. Here, we discuss the advantages of brain organoids over other model systems to study development and highlight recent advances in understanding ZIKV pathophysiology and its underlying pathogenesis mechanisms. We further discuss perspectives on overcoming limitations of current organoid systems for their future use in ZIKV research.
Keywords: Cortex; Microcephaly; Organoids; Zika; iPSC.
© 2017. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
H.N.N., H.S. and G.-l.M. are co-founders of 3Dnamics.
Figures

References
-
- Barrows N. J., Campos R. K., Powell S. T., Prasanth K. R., Schott-Lerner G., Soto-Acosta R., Galarza-Muñoz G., McGrath E. L., Urrabaz-Garza R., Gao J. et al. (2016). A screen of FDA-approved drugs for inhibitors of Zika virus infection. Cell Host Microbe 20, 259-270. 10.1016/j.chom.2016.07.004 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Calvet G., Aguiar R. S., Melo A. S. O., Sampaio S. A., de Filippis I., Fabri A., Araujo E. S. M., de Sequeira P. C., de Mendonça M. C. L., de Oliveira L. et al. (2016). Detection and sequencing of Zika virus from amniotic fluid of fetuses with microcephaly in Brazil: a case study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 16, 653-660. 10.1016/S1473-3099(16)00095-5 - DOI - PubMed
-
- CDC (2016). Zika virus. Atlanta, GA: US Department of Health and Human Services, United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; https://www.cdc.gov/zika/index.html.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

