Exploring the effect of intravenous lipid emulsion in acute methamphetamine toxicity
- PMID: 28293389
- PMCID: PMC5339653
- DOI: 10.22038/ijbms.2017.8236
Exploring the effect of intravenous lipid emulsion in acute methamphetamine toxicity
Abstract
Objectives: The increasing use of methamphetamine (METH) in the last decades has made it the second most abused drug. Advancs in the area of intravenous lipid emulsion (ILE) have led to its potential application in the treatment of poisoning. The present study aims to investigate the potential role of ILE as an antidote for acute METH poisoning.
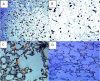
Materials and methods: Two groups of six male rats were treated by METH (45 mg/kg), intraperitoneally. Five to seven min later, they received an infusion of 18.6 ml/kg ILE 20% through the tail vein or normal saline (NS). Locomotor and behavioral activity was assessed at different time after METH administration. Body temperature and survival rates were also evaluated. Brain and internal organs were then removed for histological examination and TUNEL assay.
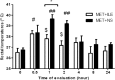
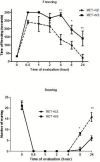
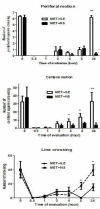
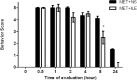
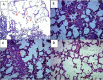
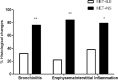
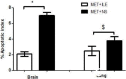
Results: ILE therapy for METH poisoning in rats could prevent rats mortalities and returned the METH-induced hyperthermia to normal rates (P<0.05). ILE reduced freezing and stereotyped behaviors and increased rearing responses (P<0.05). Locomotor activity also returned to control levels especially during the last hours of the experiment. ILE administration decreased the prevalence of pulmonary emphysema in the lungs (P<0.05 and P<0.01) and percentages of TUNEL positive cells in the brain (P<0.05), in comparison with the control group.
Conclusion: ILE could reduce the severity of METH- induced toxicity as well as mortality rate in the animals. Intravenous infusion of lipid emulsion may save the life of patients with acute METH intoxication who do not respond to standard initial therapy.
Keywords: Acute toxicity; Antidote; Intravenous lipid emulsion; Methamphetamine.
Figures
References
-
- Cadet JL, Krasnova IN, Jayanthi S, Lyles J. Neurotoxicity of substituted amphetamines: molecular and cellular mechanisms. Neurotox Res. 2007;11:183–202. - PubMed
-
- Cruickshank CC, Dyer KR. A review of the clinical pharmacology of methamphetamine. Addiction. 2009;104:1085–99. - PubMed
-
- Davis GG, Swalwell CI. The incidence of acute cocaine or methamphetamine intoxication in deaths due to ruptured cerebral (berry) aneurysms. J Forensic Sci. 1996;41:626–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
