In vitro lymphoproliferative response and cytokine production in mice with experimental disseminated candidiasis
- PMID: 28293397
- PMCID: PMC5339661
- DOI: 10.22038/ijbms.2017.8248
In vitro lymphoproliferative response and cytokine production in mice with experimental disseminated candidiasis
Abstract
Objectives: Systemic candidiasis is an infection of Candida albicans (C. albicans) causing disseminated disease and sepsis, invariably when host defenses are compromised. We investigated the histopathological changes as well as the lymphoproliferative responses and cytokine production of splenic cells after stimulation with Concanavalin A (Con A) and Pokeweed mitogen (PWM) in mice with disseminated candidiasis.
Materials and methods: Lymphoproliferative responses were stimulated in vitro with Con A (1 µg/ml) and PWM (1 µg/ml) mitogens in Roswell Park Memorial Institute (RPMI) 1640 media, and the production of interferon (IFN)-γ and interleukin-4 (IL-4) in the supernatants was measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
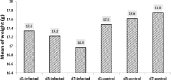
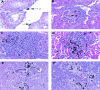
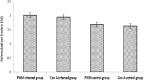
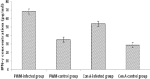
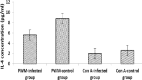
Results: The results revealed that C. albicans organisms multiplied to a greater extent in the kidneys than in the liver and spleen of infected mice. The most predominant forms of C. albicans in different parts of the kidneys were yeast mixed with hyphal forms. Infected mice had a significantly increased proliferative response when splenocytes were stimulated with PWM (2.0±0.16) and Con A (1.9±0.19) (P<0.05). PWM and Con A-stimulated production of IFN-γ significantly tended to be higher in infected mice (PWM: 68.4±14.0 pg/ml; Con A: 53.7±17.3 pg/ml) when compared to controls (P<0.05). Stimulation with PWM and Con A showed no differences in IL-4 production between infected mice and controls.
Conclusion: These findings demonstrated a significant increase in both cell proliferation and IFN-γ secretion in supernatants of PWM and Con A- stimulated splenocyte cultures obtained from mice with disseminated candidiasis.
Keywords: Candida albicans; Cytokine production; Lymphocyte proliferation; Mice; Mitogens; Systemic candidiasis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mitogen-Induced Interferon Gamma Production in Human Whole Blood: The Effect of Heat and Cations.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2019;20(7):562-572. doi: 10.2174/1389201020666190528093432. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 31132974
-
Evaluation of proliferation and cytokines production by mitogen-stimulated bovine peripheral blood mononuclear cells.Vet Res Forum. 2015 Fall;6(4):265-71. Epub 2015 Dec 15. Vet Res Forum. 2015. PMID: 26973760 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of pathogenesis and host immune responses to Candida glabrata and Candida albicans in systemically infected immunocompetent mice.Infect Immun. 2001 Aug;69(8):5046-55. doi: 10.1128/IAI.69.8.5046-5055.2001. Infect Immun. 2001. PMID: 11447185 Free PMC article.
-
Propolis efficacy on TNF-α, IFN-γ and IL2 cytokines production in old mice with and without systemic candidiasis.J Mycol Med. 2012 Sep;22(3):237-42. doi: 10.1016/j.mycmed.2012.05.004. Epub 2012 Aug 9. J Mycol Med. 2012. PMID: 23518081
-
Gamma interferon is not essential in host defense against disseminated candidiasis in mice.Infect Immun. 1997 May;65(5):1748-53. doi: 10.1128/iai.65.5.1748-1753.1997. Infect Immun. 1997. PMID: 9125557 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Calderone RA. Candida and Candidiasis. New York: American Society for Microbiology; 2001.
-
- Garber G. An overview of fungal infections. Drugs. 2001;61:1–12. - PubMed
-
- Romani L, Mencacci A, Cenci E, Del Sero G, Bistoni F, Puccetti P. An immunoregulatory role for neutrophils in CD41 T helper subset selection in mice with candidiasis. J Immunol. 1997;158:2356–2362. - PubMed
-
- O’Garra A. Cytokines induce the development of functionally heterogeneous T helper cell subsets. Immun. 1998;8:275–283. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
