Visual Motor and Perceptual Task Performance in Astigmatic Students
- PMID: 28293434
- PMCID: PMC5331474
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/6460281
Visual Motor and Perceptual Task Performance in Astigmatic Students
Abstract
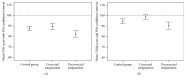
Purpose. To determine if spectacle corrected and uncorrected astigmats show reduced performance on visual motor and perceptual tasks. Methods. Third through 8th grade students were assigned to the low refractive error control group (astigmatism < 1.00 D, myopia < 0.75 D, hyperopia < 2.50 D, and anisometropia < 1.50 D) or bilateral astigmatism group (right and left eye ≥ 1.00 D) based on cycloplegic refraction. Students completed the Beery-Buktenica Developmental Test of Visual Motor Integration (VMI) and Visual Perception (VMIp). Astigmats were randomly assigned to testing with/without correction and control group was tested uncorrected. Analyses compared VMI and VMIp scores for corrected and uncorrected astigmats to the control group. Results. The sample included 333 students (control group 170, astigmats tested with correction 75, and astigmats tested uncorrected 88). Mean VMI score in corrected astigmats did not differ from the control group (p = 0.829). Uncorrected astigmats had lower VMI scores than the control group (p = 0.038) and corrected astigmats (p = 0.007). Mean VMIp scores for uncorrected (p = 0.209) and corrected astigmats (p = 0.124) did not differ from the control group. Uncorrected astigmats had lower mean scores than the corrected astigmats (p = 0.003). Conclusions. Uncorrected astigmatism influences visual motor and perceptual task performance. Previously spectacle treated astigmats do not show developmental deficits on visual motor or perceptual tasks when tested with correction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

