Learning and memory disabilities in IUGR babies: Functional and molecular analysis in a rat model
- PMID: 28293472
- PMCID: PMC5346519
- DOI: 10.1002/brb3.631
Learning and memory disabilities in IUGR babies: Functional and molecular analysis in a rat model
Abstract
Introduction: 1Intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR) is the failure of the fetus to achieve its inherent growth potential, and it has frequently been associated with neurodevelopmental problems in childhood. Neurological disorders are mostly associated with IUGR babies with an abnormally high cephalization index (CI) and a brain sparing effect. However, a similar correlation has never been demonstrated in an animal model. The aim of this study was to determine the correlations between CI, functional deficits in learning and memory and alterations in synaptic proteins in a rat model of IUGR.
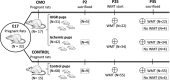
Methods: 2Utero-placental insufficiency was induced by meso-ovarian vessel cauterization (CMO) in pregnant rats at embryonic day 17 (E17). Learning performance in an aquatic learning test was evaluated 25 days after birth and during 10 days. Some synaptic proteins were analyzed (PSD95, Synaptophysin) by Western blot and immunohistochemistry.
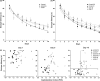
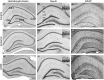
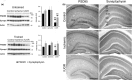
Results: 3Placental insufficiency in CMO pups was associated with spatial memory deficits, which are correlated with a CI above the normal range. CMO pups presented altered levels of synaptic proteins PSD95 and synaptophysin in the hippocampus.
Conclusions: 4The results of this study suggest that learning disabilities may be associated with altered development of excitatory neurotransmission and synaptic plasticity. Although interspecific differences in fetal response to placental insufficiency should be taken into account, the translation of these data to humans suggest that both IUGR babies and babies with a normal birth weight but with intrauterine Doppler alterations and abnormal CI should be closely followed to detect neurodevelopmental alterations during the postnatal period.
Keywords: cephalization index; intrauterine growth restriction; learning; placental insufficiency; spatial memory; synaptic plasticity.
Figures
References
-
- Arcangeli, T. , Thilaganathan, B. , Hooper, R. , Khan, K. S. , & Bhide, A. (2012). Neurodevelopmental delay in small babies at term: A systematic review. Ultrasound in Obstetrics and Gynecology, 40, 267–275. - PubMed
-
- Barrow, P. , & Leconte, I. (1996). The influence of body weight on open field and swimming maze performance during the post‐weaning period in the rat. Laboratory Animals, 30, 22–27. - PubMed
-
- de Bie, H. M. , Oostrom, K. J. , & Delemarre‐van de Waal, H. A. (2010). Brain development, intelligence and cognitive outcome in children born small for gestational age. Hormone Research in Pædiatrics, 73, 6–14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

