Aesthetic Applications of Botulinum Toxin A in Asians: An International, Multidisciplinary, Pan-Asian Consensus
- PMID: 28293488
- PMCID: PMC5222633
- DOI: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000000507
Aesthetic Applications of Botulinum Toxin A in Asians: An International, Multidisciplinary, Pan-Asian Consensus
Abstract
Background: Botulinum toxin type A remains the most popular nonsurgical aesthetic treatment worldwide. Previous consensus statements have focused on Caucasians and on Koreans as generally representative of Asians. However, indications and dosages vary among different ethnic groups. This publication reports the results of a multidisciplinary, pan-Asian consensus focusing on incobotulinumtoxinA.
Methods: A consensus group of plastic surgeons and dermatologists from Asia, Europe, and the United States convened for a live meeting in Asia, followed by a questionnaire-based Delphi procedure. Treatment of Asians in both their native countries and countries of migration was discussed.
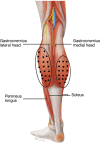
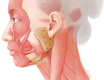
Results: For most items, the group achieved a majority consensus. A number of treatment indications, strategies, and dosages were identified in Asians, which are distinct to those previously described for Caucasians due to differences in facial morphotypes, anatomy, and cultural expectations. The group also formulated position statements for intradermal botulinum toxin type A ("mesotoxin"), body shaping with the calves as a paradigm, and reduction of parotid glands. While Asians have previously been considered a homogeneous group for the purposes of aesthetic treatment, this publication considers regional variations. A new classification of Asian facial morphotypes is proposed to aid treatment planning and implementation.
Conclusions: This is the first pan-Asian consensus for aesthetic use of botulinum toxin type A. Its unique objective is to optimize treatment safety and efficacy for patients of complete or part-Asian ancestry in all regions. The recommendations for incobotulinumtoxinA may be extended with care to other botulinum toxin formulations.
Figures
References
-
- Ascher B, Talarico S, Cassuto D, et al. International consensus recommendations on the aesthetic usage of botulinum toxin type A (Speywood Unit)–Part II: Wrinkles on the middle and lower face, neck and chest. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2010;24:1285–1295. - PubMed
-
- Ascher B, Talarico S, Cassuto D, et al. International consensus recommendations on the aesthetic usage of botulinum toxin type A (Speywood Unit)–Part I: Upper facial wrinkles. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2010;24:1278–1284. - PubMed
-
- Carruthers A, Kane MA, Flynn TC, et al. The convergence of medicine and neurotoxins: a focus on botulinum toxin type A and its application in aesthetic medicine–a global, evidence-based botulinum toxin consensus education initiative: part I: botulinum toxin in clinical and cosmetic practice. Dermatol Surg. 2013;39(3 Pt 2):493–509. - PubMed
-
- Carruthers J, Fagien S, Matarasso SL Botox Consensus Group. Consensus recommendations on the use of botulinum toxin type a in facial aesthetics. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2004;114(6 Suppl):1S–22S. - PubMed
-
- Carruthers J, Fournier N, Kerscher M, et al. The convergence of medicine and neurotoxins: a focus on botulinum toxin type A and its application in aesthetic medicine–a global, evidence-based botulinum toxin consensus education initiative: part II: incorporating botulinum toxin into aesthetic clinical practice. Dermatol Surg. 2013;39(3 Pt 2):510–525. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
