Suppression of murine tumour growth through CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes via activated DEC-205+ dendritic cells by sequential administration of α-galactosylceramide in vivo
- PMID: 28294313
- PMCID: PMC5461099
- DOI: 10.1111/imm.12733
Suppression of murine tumour growth through CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes via activated DEC-205+ dendritic cells by sequential administration of α-galactosylceramide in vivo
Abstract
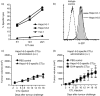
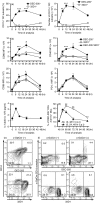
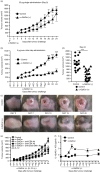
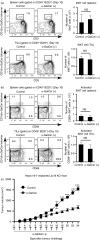
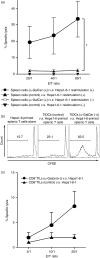
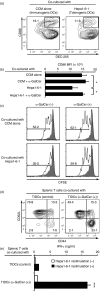
Cancer immunity is mediated through the effective priming and activation of tumour-specific class I MHC molecule-restricted CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs). DEC-205+ dendritic cells (DCs) can cross-present the epitope(s) of captured tumour antigens associated with class I MHC molecules alongside co-stimulatory molecules to prime and activate tumour-specific CD8+ CTLs. Immunosuppressive tolerogenic DCs with reduced co-stimulatory molecules may be a cause of impaired CTL induction. Hepa1-6-1 cells were established from the mouse hepatoma cell line Hepa1-6; these cells grow continuously after subcutaneous implantation into syngeneic C57BL/6 (B6) mice and do not prime CD8+ CTLs. In this study, we show that the growth of ongoing tumours was suppressed by activated CD8+ CTLs with tumour-specific cytotoxicity through the administration of the glycolipid α-galactosylceramide (α-GalCer), which is a compound known to stimulate invariant natural killer T (iNKT) cells and selectively activate DEC-205+ DCs. Moreover, we demonstrated that sequential repetitive intraperitoneal inoculation with α-GalCer every 48 hr appeared to convert tolerogenic DEC-205+ DCs into immunogenic DCs with a higher expression of co-stimulatory molecules and a stronger cross-presentation capacity, which primed CTL precursors and induced tumour-specific CD8+ CTLs within the tumour environment without activating iNKT cells. These findings provide a new basis for cancer immunotherapy to convert tolerogenic DEC-205+ DCs within tumours into immunogenic DCs through the sequential administration of an immuno-potent lipid/glycolipid, and then activated immunogenic DCs with sufficient expression of co-stimulatory molecules prime and activate tumour-specific CD8+ CTLs within the tumour to control tumour growth.
Keywords: co-stimulatory molecule; cytotoxic T lymphocytes; tumour-infiltrating dendritic cells; tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes; α-galactosylceramide.
© 2017 The Authors. Immunology Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Buller RM, Holmes KL, Hugin A, Frederickson TN, Morse HC 3rd. Induction of cytotoxic T‐cell responses in vivo in the absence of CD4 helper cells. Nature 1987; 328:77–9. - PubMed
-
- Germain RN. MHC‐dependent antigen processing and peptide presentation: providing ligands for T lymphocyte activation. Cell 1994; 76:287–99. - PubMed
-
- Takahashi H. Antigen presentation in vaccine development. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis 2003; 26:309–28. - PubMed
-
- Takahashi H, Takeshita T, Morein B, Putney S, Germain RN, Berzofsky JA. Induction of CD8+ cytotoxic T cells by immunization with purified HIV‐1 envelope protein in ISCOMs. Nature 1990; 344:873–5. - PubMed
-
- Takahashi H, Nakagawa Y, Yokomuro K, Berzofsky JA. Induction of CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes by immunization with syngeneic irradiated HIV‐1 envelope derived peptide‐pulsed dendritic cells. Int Immunol 1993; 5:849–57. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

