Avoiding disentanglement of multipartite entangled optical beams with a correlated noisy channel
- PMID: 28295024
- PMCID: PMC5353719
- DOI: 10.1038/srep44475
Avoiding disentanglement of multipartite entangled optical beams with a correlated noisy channel
Abstract
A quantum communication network can be constructed by distributing a multipartite entangled state to space-separated nodes. Entangled optical beams with highest flying speed and measurable brightness can be used as carriers to convey information in quantum communication networks. Losses and noises existing in real communication channels will reduce or even totally destroy entanglement. The phenomenon of disentanglement will result in the complete failure of quantum communication. Here, we present the experimental demonstrations on the disentanglement and the entanglement revival of tripartite entangled optical beams used in a quantum network. We experimentally demonstrate that symmetric tripartite entangled optical beams are robust in pure lossy but noiseless channels. In a noisy channel, the excess noise will lead to the disentanglement and the destroyed entanglement can be revived by the use of a correlated noisy channel (non-Markovian environment). The presented results provide useful technical references for establishing quantum networks.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
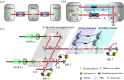
 and
and  ) of a tripartite entangled state are distributed over two lossy quantum channels to Alice and Claire, respectively. (b) One mode of the tripartite entangled state is distributed over a noisy channel, where disentanglement is observed among optical modes
) of a tripartite entangled state are distributed over two lossy quantum channels to Alice and Claire, respectively. (b) One mode of the tripartite entangled state is distributed over a noisy channel, where disentanglement is observed among optical modes  and
and  . The entanglement revival operation is implemented by coupling an ancillary beam (
. The entanglement revival operation is implemented by coupling an ancillary beam ( ) who has correlated noise with the environment with the transmitted mode
) who has correlated noise with the environment with the transmitted mode  on a beam-splitter with transmission efficiency of
on a beam-splitter with transmission efficiency of  , thus the entanglement among modes
, thus the entanglement among modes  ,
,  and
and  is revived. (c) The schematic of experimental set-up for distributing a mode of the tripartite entangled optical beams over a noisy channel and the entanglement revival. T1 and T2 are the beam-splitters used to generate the GHZ entangled state. ηA and T are the transmission efficiencies of the noisy channel and the revival beam-splitter, respectively. HD1-3, homodyne detectors. LO, the local oscillator.
is revived. (c) The schematic of experimental set-up for distributing a mode of the tripartite entangled optical beams over a noisy channel and the entanglement revival. T1 and T2 are the beam-splitters used to generate the GHZ entangled state. ηA and T are the transmission efficiencies of the noisy channel and the revival beam-splitter, respectively. HD1-3, homodyne detectors. LO, the local oscillator.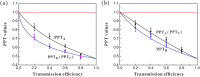
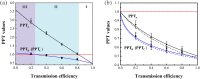
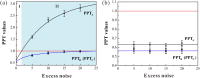
 is distributed in the lossy channel (ηA ≠ 1, ηC = 1). (b) Two optical modes
is distributed in the lossy channel (ηA ≠ 1, ηC = 1). (b) Two optical modes  and
and  are distributed in the lossy channels with the same transmission efficiency (ηA ≠ 1, ηC ≠ 1). PPT values are all below the entanglement boundary (red lines), which means that the tripartite entanglement is robust against loss in quantum channels. The black, blue and pink dots represent the experimental data for different PPT values, respectively. Error bars represent ± one standard deviation and are obtained based on the statistics of the measured noise variances.
are distributed in the lossy channels with the same transmission efficiency (ηA ≠ 1, ηC ≠ 1). PPT values are all below the entanglement boundary (red lines), which means that the tripartite entanglement is robust against loss in quantum channels. The black, blue and pink dots represent the experimental data for different PPT values, respectively. Error bars represent ± one standard deviation and are obtained based on the statistics of the measured noise variances.
Similar articles
-
Quantum Entanglement Swapping between Two Multipartite Entangled States.Phys Rev Lett. 2016 Dec 9;117(24):240503. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.117.240503. Epub 2016 Dec 6. Phys Rev Lett. 2016. PMID: 28009187
-
Establishing and storing of deterministic quantum entanglement among three distant atomic ensembles.Nat Commun. 2017 Sep 28;8(1):718. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-00809-9. Nat Commun. 2017. PMID: 28959032 Free PMC article.
-
Asymptotic Survival of Genuine Multipartite Entanglement in Noisy Quantum Networks Depends on the Topology.Phys Rev Lett. 2022 Jun 3;128(22):220501. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.128.220501. Phys Rev Lett. 2022. PMID: 35714237
-
Three-color entanglement.Science. 2009 Nov 6;326(5954):823-6. doi: 10.1126/science.1178683. Epub 2009 Sep 17. Science. 2009. PMID: 19762598
-
Measurement-Device-Independent Entanglement Witness of Tripartite Entangled States and Its Applications.Phys Rev Lett. 2020 Apr 24;124(16):160503. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.124.160503. Phys Rev Lett. 2020. PMID: 32383895
Cited by
-
Control Power in Continuous Variable Controlled Quantum Teleportation.Entropy (Basel). 2024 Nov 25;26(12):1017. doi: 10.3390/e26121017. Entropy (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39766646 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nielson M. A. & Chuang I. L. Quantum Computation And Quantum Information. (Cambridge University, Cambridge, 2000).
-
- Ralph T. C. & Lam P. K. A bright future for quantum communications. Nat. Photon. 3, 671–673 (2009).
-
- Braunstein S. L. & van Loock P. Quantum information with continuous variables. Rev. Mod. Phys. 77, 513–577 (2005).
-
- Weedbrook C. et al.. Gaussian quantum information. Rev. Mod. Phys. 84, 621–669 (2012).
-
- Raussendorf R. & Briegel H. J. A one-way quantum computer. Phys. Rev. Lett. 86, 5188–5191 (2001). - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

