Gonadal mosaicism of a novel IQSEC2 variant causing female limited intellectual disability and epilepsy
- PMID: 28295038
- PMCID: PMC5477359
- DOI: 10.1038/ejhg.2017.29
Gonadal mosaicism of a novel IQSEC2 variant causing female limited intellectual disability and epilepsy
Abstract
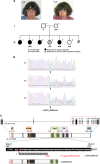
We report a family with four girls with moderate to severe intellectual disability and epilepsy. Two girls showed regression in adolescence and died of presumed sudden unexpected death in epilepsy at 16 and 22 years. Whole exome sequencing identified a truncating pathogenic variant in IQSEC2 at NM_001111125.2: c.2679_2680insA, p.(D894fs*10), a recently identified cause of epileptic encephalopathy in females (MIM 300522). The IQSEC2 variant was identified in both surviving affected sisters but in neither parent. We describe the phenotypic spectrum associated with IQSEC2 variants, highlighting how IQSEC2 is adding to a growing list of X-linked genes that have a female-specific phenotype typically associated with de novo mutations. This report illustrates the need for careful review of all whole exome data, incorporating all possible modes of inheritance including that suggested by the family history.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Rauch A, Wieczorek D, Graf E et al: Range of genetic mutations associated with severe non-syndromic sporadic intellectual disability: an exome sequencing study. Lancet 2012; 380: 1674–1682. - PubMed
-
- Gandomi SK, Farwell Gonzalez KD, Parra M et al: Diagnostic exome sequencing identifies two novel IQSEC2 mutations associated with X-linked intellectual disability with seizures: implications for genetic counseling and clinical diagnosis. J Genet Counsel 2014; 23: 289–298. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

