Targeting C3a/C5a receptors inhibits human mesangial cell proliferation and alleviates immunoglobulin A nephropathy in mice
- PMID: 28295247
- PMCID: PMC5461107
- DOI: 10.1111/cei.12961
Targeting C3a/C5a receptors inhibits human mesangial cell proliferation and alleviates immunoglobulin A nephropathy in mice
Abstract
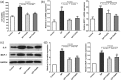
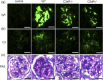
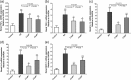
Complement activation has a deep pathogenic influence in immunoglobulin (Ig)A nephropathy (IgAN). C3a and C5a, small cleavage fragments generated by complement activation, are key mediators of inflammation. The fragments exert broad proinflammatory effects by binding to specific receptors (C3aR and C5aR, respectively). However, no studies thus far have investigated the effects of C3a, C5a and their receptors on IgAN. We observed that C3aR and C5aR antagonists repressed IgA-induced cell proliferation and interleukin (IL)-6 and monocyte chemotactic protein 1 (MCP-1) production in cultured human mesangial cells (HMCs). Furthermore, an IgAN mouse model induced by Sendai virus infection was employed to investigate the effects of C3aR and C5aR on IgAN in vivo for the first time. Wild-type (WT) and several knock-out mouse strains (C3aR-/- or C5aR-/- ) were immunized intranasally with increasing doses of inactivated virus for 14 weeks and were subjected to two intravenous viral challenges during the time-period indicated. In the Sendai virus-induced IgAN model, C3aR/C5aR-deficient mice had significantly reduced proteinuria, lower renal IgA and C3 deposition, less histological damage and reduced mesangial proliferation compared with WT mice. Both C3aR deficiency and C5aR deficiency, especially C3aR deficiency, inhibited renal tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-α, transforming growth factor (TGF)-β, IL-1β, IL-6 and MCP-1 expression significantly. However, C3aR/C5aR-deficient and WT mice with IgAN did not differ with respect to their blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and serum creatinine levels. Our findings provide further support for the idea that C3aR and C5aR are crucially important in IgAN, and suggest that pharmaceutically targeting C3aR/C5aR may hold promise for the treatment of IgAN.
Keywords: C3a receptor; C5a receptor; IgA nephropathy; complement.
© 2017 British Society for Immunology.
Figures

Similar articles
-
C3a, C5a renal expression and their receptors are correlated to severity of IgA nephropathy.J Clin Immunol. 2014 Feb;34(2):224-32. doi: 10.1007/s10875-013-9970-6. Epub 2013 Dec 12. J Clin Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24327134
-
Complement C3a/C3aR and C5a/C5aR deposits accelerate the progression of advanced IgA nephropathy to end-stage renal disease.Clin Exp Med. 2024 Jun 29;24(1):139. doi: 10.1007/s10238-024-01410-3. Clin Exp Med. 2024. PMID: 38951265 Free PMC article.
-
Mast cell anaphylatoxin receptor expression can enhance IgE-dependent skin inflammation in mice.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013 Feb;131(2):541-8.e1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2012.05.009. Epub 2012 Jun 22. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013. PMID: 22728083 Free PMC article.
-
The Complement C3a and C5a Signaling in Renal Diseases: A Bridge between Acute and Chronic Inflammation.Nephron. 2024;148(10):712-723. doi: 10.1159/000538241. Epub 2024 Mar 8. Nephron. 2024. PMID: 38452744 Review.
-
The role of anaphylatoxins C3a and C5a in regulating innate and adaptive immune responses.Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets. 2009 Jul;8(3):236-46. doi: 10.2174/187152809788681038. Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets. 2009. PMID: 19601884 Review.
Cited by
-
Potential Mechanisms Underlying TGF-β-mediated Complement Activation in Lung Fibrosis.Cell Mol Med Open Access. 2017;3(3):14. doi: 10.21767/2573-5365.100037. Epub 2017 Nov 22. Cell Mol Med Open Access. 2017. PMID: 29377033 Free PMC article.
-
An Update on Targeted Treatment of IgA Nephropathy: An Autoimmune Perspective.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Aug 23;12:715253. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.715253. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34497518 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune-mediated renal injury in diabetic kidney disease: from mechanisms to therapy.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 4;16:1587806. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1587806. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40534883 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New Insights Regarding Diagnosis and Medication for Schizophrenia Based on Neuronal Synapse-Microglia Interaction.J Pers Med. 2021 May 3;11(5):371. doi: 10.3390/jpm11050371. J Pers Med. 2021. PMID: 34063598 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Low-molecular weight inhibitors of the alternative complement pathway.Immunol Rev. 2023 Jan;313(1):339-357. doi: 10.1111/imr.13143. Epub 2022 Oct 11. Immunol Rev. 2023. PMID: 36217774 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Berthoux FC, Mohey H, Afiani A. Natural history of primary IgA nephropathy. Semin Nephrol 2008; 28:4–9. - PubMed
-
- Kidney D. Improving global outcomes (KDIGO) glomerulonephritis work group. KDIGO clinical practice guideline for glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int Suppl 2012; 2:139–274.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

