Outcomes of adults with relapsed or refractory Burkitt and high-grade B-cell leukemia/lymphoma
- PMID: 28295472
- PMCID: PMC5828013
- DOI: 10.1002/ajh.24720
Outcomes of adults with relapsed or refractory Burkitt and high-grade B-cell leukemia/lymphoma
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
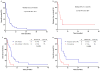
References
-
- Ferry JA. Burkitt’s lymphoma: clinicopathologic features and differential diagnosis. The oncologist. 2006;11:375–383. - PubMed
-
- Thomas DA, Faderl S, O’Brien S, et al. Chemoimmunotherapy with hyper-CVAD plus rituximab for the treatment of adult Burkitt and Burkitt-type lymphoma or acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer. 2006;106:1569–1580. - PubMed
-
- Ribrag V, Koscielny S, Bosq J, et al. Rituximab and dose-dense chemotherapy for adults with Burkitt’s lymphoma: a randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2016;387:2402–2411. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
