Intracoronary allogeneic cardiosphere-derived stem cells are safe for use in dogs with dilated cardiomyopathy
- PMID: 28296006
- PMCID: PMC5543505
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.13077
Intracoronary allogeneic cardiosphere-derived stem cells are safe for use in dogs with dilated cardiomyopathy
Abstract
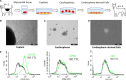
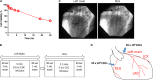
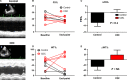
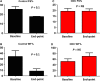
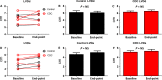
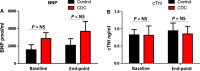
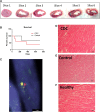
Cardiosphere-derived cells (CDCs) have been shown to reduce scar size and increase viable myocardium in human patients with mild/moderate myocardial infarction. Studies in rodent models suggest that CDC therapy may confer therapeutic benefits in patients with non-ischaemic dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM). We sought to determine the safety and efficacy of allogeneic CDC in a large animal (canine) model of spontaneous DCM. Canine CDCs (cCDCs) were grown from a donor dog heart. Similar to human CDCs, cCDCs express CD105 and are slightly positive for c-kit and CD90. Thirty million of allogeneic cCDCs was infused into the coronary vessels of Doberman pinscher dogs with spontaneous DCM. Adverse events were closely monitored, and cardiac functions were measured by echocardiography. No adverse events occurred during and after cell infusion. Histology on dog hearts (after natural death) revealed no sign of immune rejection from the transplanted cells.
Keywords: allogeneic; cardiosphere-derived cells; dilated cardiomyopathy; dogs; stem cell therapy.
© 2017 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd and Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cardiac regenerative potential of cardiosphere-derived cells from adult dog hearts.J Cell Mol Med. 2015 Aug;19(8):1805-13. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12585. Epub 2015 Apr 9. J Cell Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 25854418 Free PMC article.
-
Cryopreservation of canine cardiosphere-derived cells: Implications for clinical application.Cytometry A. 2018 Jan;93(1):115-124. doi: 10.1002/cyto.a.23186. Epub 2017 Aug 22. Cytometry A. 2018. PMID: 28834400
-
Cardiosphere-Derived Cells Attenuate Inflammation, Preserve Systolic Function, and Prevent Adverse Remodeling in Rat Hearts With Experimental Autoimmune Myocarditis.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 2019 Jan;24(1):70-77. doi: 10.1177/1074248418784287. Epub 2018 Jul 30. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 2019. PMID: 30060693
-
Cardiosphere-Derived Cells and Ischemic Heart Failure.Cardiol Rev. 2018 Jan/Feb;26(1):8-21. doi: 10.1097/CRD.0000000000000173. Cardiol Rev. 2018. PMID: 29206745 Review.
-
Histologic characterization of canine dilated cardiomyopathy.Vet Pathol. 2005 Jan;42(1):1-8. doi: 10.1354/vp.42-1-1. Vet Pathol. 2005. PMID: 15657266 Review.
Cited by
-
Cardiac Cell Therapy for Heart Repair: Should the Cells Be Left Out?Cells. 2021 Mar 13;10(3):641. doi: 10.3390/cells10030641. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33805763 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic benefits of CD90-negative cardiac stromal cells in rats with a 30-day chronic infarct.J Cell Mol Med. 2018 Mar;22(3):1984-1991. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13517. Epub 2018 Jan 17. J Cell Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 29341439 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiology's best friend: Using naturally occurring disease in dogs to understand heart disease in humans.J Mol Cell Cardiol Plus. 2025 Jul 4;13:100474. doi: 10.1016/j.jmccpl.2025.100474. eCollection 2025 Sep. J Mol Cell Cardiol Plus. 2025. PMID: 40686503 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Infant cardiosphere-derived cells exhibit non-durable heart protection in dilated cardiomyopathy rats.Cytotechnology. 2019 Dec;71(6):1043-1052. doi: 10.1007/s10616-019-00328-z. Epub 2019 Oct 3. Cytotechnology. 2019. PMID: 31583508 Free PMC article.
-
ISL1 overexpression enhances the survival of transplanted human mesenchymal stem cells in a murine myocardial infarction model.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018 Feb 26;9(1):51. doi: 10.1186/s13287-018-0803-7. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018. PMID: 29482621 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mozaffarian D, Benjamin EJ, Go AS, et al ; on behalf of the American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee . Heart disease and stroke statistics— 2015 update: a report from the American Heart Association [published online ahead of print December 17, 2014]. Circulation 2015; 131: e29–e322. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000152. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cesselli D, Jakoniuk I, Barlucchi L, et al Oxidative stress‐mediated cardiac cell death is a major determinant of ventricular dysfunction and failure in dog dilated cardiomyopathy. Circ Res. 2001; 89: 279–86. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

