DIMP53-1: a novel small-molecule dual inhibitor of p53-MDM2/X interactions with multifunctional p53-dependent anticancer properties
- PMID: 28296148
- PMCID: PMC5467495
- DOI: 10.1002/1878-0261.12051
DIMP53-1: a novel small-molecule dual inhibitor of p53-MDM2/X interactions with multifunctional p53-dependent anticancer properties
Abstract
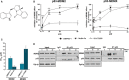
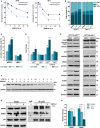
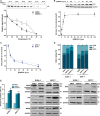
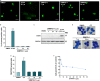
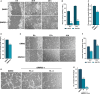
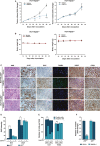
The transcription factor p53 plays a crucial role in cancer development and dissemination, and thus, p53-targeted therapies are among the most encouraging anticancer strategies. In human cancers with wild-type (wt) p53, its inactivation by interaction with murine double minute (MDM)2 and MDMX is a common event. Simultaneous inhibition of the p53 interaction with both MDMs is crucial to restore the tumor suppressor activity of p53. Here, we describe the synthesis of the new tryptophanol-derived oxazoloisoindolinone DIMP53-1 and identify its activity as a dual inhibitor of the p53-MDM2/X interactions using a yeast-based assay. DIMP53-1 caused growth inhibition, mediated by p53 stabilization and upregulation of p53 transcriptional targets involved in cell cycle arrest and apoptosis, in wt p53-expressing tumor cells, including MDM2- or MDMX-overexpressing cells. Importantly, DIMP53-1 inhibits the p53-MDM2/X interactions by potentially binding to p53, in human colon adenocarcinoma HCT116 cells. DIMP53-1 also inhibited the migration and invasion of HCT116 cells, and the migration and tube formation of HMVEC-D endothelial cells. Notably, in human tumor xenograft mice models, DIMP53-1 showed a p53-dependent antitumor activity through induction of apoptosis and inhibition of proliferation and angiogenesis. Finally, no genotoxicity or undesirable toxic effects were observed with DIMP53-1. In conclusion, DIMP53-1 is a novel p53 activator, which potentially binds to p53 inhibiting its interaction with MDM2 and MDMX. Although target-directed, DIMP53-1 has a multifunctional activity, targeting major hallmarks of cancer through its antiproliferative, proapoptotic, antiangiogenic, anti-invasive, and antimigratory properties. DIMP53-1 is a promising anticancer drug candidate and an encouraging starting point to develop improved derivatives for clinical application.
Keywords: MDMX; MDM2; anticancer therapy; p53; small-molecule; tryptophanol-derived oxazoloisoindolinone.
© 2017 The Authors. Published by FEBS Press and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A tryptophanol-derived oxazolopiperidone lactam is cytotoxic against tumors via inhibition of p53 interaction with murine double minute proteins.Pharmacol Res. 2015 May-Jun;95-96:42-52. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2015.03.006. Epub 2015 Mar 23. Pharmacol Res. 2015. PMID: 25814188
-
Oxazoloisoindolinones with in vitro antitumor activity selectively activate a p53-pathway through potential inhibition of the p53-MDM2 interaction.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2015 Jan 23;66:138-47. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2014.10.006. Epub 2014 Oct 13. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2015. PMID: 25312347
-
Reactivation of wild-type and mutant p53 by tryptophanolderived oxazoloisoindolinone SLMP53-1, a novel anticancer small-molecule.Oncotarget. 2016 Jan 26;7(4):4326-43. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6775. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26735173 Free PMC article.
-
Medicinal Chemistry Strategies to Disrupt the p53-MDM2/MDMX Interaction.Med Res Rev. 2016 Sep;36(5):789-844. doi: 10.1002/med.21393. Epub 2016 Jun 15. Med Res Rev. 2016. PMID: 27302609 Review.
-
MDM2/X inhibitors under clinical evaluation: perspectives for the management of hematological malignancies and pediatric cancer.J Hematol Oncol. 2017 Jul 3;10(1):133. doi: 10.1186/s13045-017-0500-5. J Hematol Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28673313 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
TP53 in bone and soft tissue sarcomas.Pharmacol Ther. 2019 Oct;202:149-164. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2019.06.010. Epub 2019 Jul 2. Pharmacol Ther. 2019. PMID: 31276706 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting Transcription Factors for Cancer Treatment.Molecules. 2018 Jun 19;23(6):1479. doi: 10.3390/molecules23061479. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 29921764 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SLMP53-2 Restores Wild-Type-Like Function to Mutant p53 through Hsp70: Promising Activity in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Aug 10;11(8):1151. doi: 10.3390/cancers11081151. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31405179 Free PMC article.
-
Norhierridin B, a New Hierridin B-Based Hydroquinone with Improved Antiproliferative Activity.Molecules. 2020 Mar 30;25(7):1578. doi: 10.3390/molecules25071578. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32235535 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoglycaemic and Antioxidant Properties of Acrocomia aculeata (Jacq.) Lodd Ex Mart. Extract Are Associated with Better Vascular Function of Type 2 Diabetic Rats.Nutrients. 2021 Aug 20;13(8):2856. doi: 10.3390/nu13082856. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34445015 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baeriswyl V and Christofori G (2009) The angiogenic switch in carcinogenesis. Semin Cancer Biol 19, 329–337. - PubMed
-
- Cordani M, Pacchiana R, Butera G, D'Orazi G, Scarpa A and Donadelli M (2016) Mutant p53 proteins alter cancer cell secretome and tumour microenvironment: involvement in cancer invasion and metastasis. Cancer Lett 376, 303–309. - PubMed
-
- Gomes S, Leao M, Raimundo L, Ramos H, Soares J and Saraiva L (2016) p53 family interactions and yeast: together in anticancer therapy. Drug Discov Today 21, 616–624. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

