Foxp3+ Regulatory T Cell Expression of Keratinocyte Growth Factor Enhances Lung Epithelial Proliferation
- PMID: 28296468
- PMCID: PMC5576587
- DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2017-0019OC
Foxp3+ Regulatory T Cell Expression of Keratinocyte Growth Factor Enhances Lung Epithelial Proliferation
Abstract
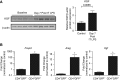
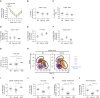
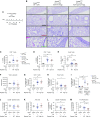
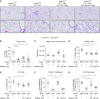
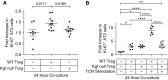
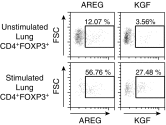
Repair of the lung epithelium after injury is a critical component for resolution; however, the processes necessary to drive epithelial resolution are not clearly defined. Published data demonstrate that Foxp3+ regulatory T cells (Tregs) enhance alveolar epithelial proliferation after injury, and Tregs in vitro directly promote type II alveolar epithelial cell (AT2) proliferation, in part by a contact-independent mechanism. Therefore, we sought to determine the contribution of Treg-specific expression of a growth factor that is known to be important in lung repair, keratinocyte growth factor (kgf). The data demonstrate that Tregs express kgf and that Treg-specific expression of kgf regulates alveolar epithelial proliferation during the resolution phase of acute lung injury and in a model of regenerative alveologenesis in vivo. In vitro experiments demonstrate that AT2 cells cocultured with Tregs lacking kgf have decreased rates of proliferation compared with AT2 cells cocultured with wild-type Tregs. Moreover, Tregs isolated from lung tissue and grown in culture express higher levels of two growth factors that are important for lung repair (kgf and amphiregulin) compared with Tregs isolated from splenic tissue. Lastly, Tregs isolated from human lung tissue can be stimulated ex vivo to induce kgf expression. This study reveals mechanisms by which Tregs direct tissue-reparative effects during resolution after acute lung injury, further supporting the emerging role of Tregs in tissue repair.
Keywords: Foxp3; acute lung injury; alveolar epithelial repair; keratinocyte growth factor; regulatory T cells.
Figures

References
-
- Kieran NE, Maderna P, Godson C. Lipoxins: potential anti-inflammatory, proresolution, and antifibrotic mediators in renal disease. Kidney Int. 2004;65:1145–1154. - PubMed
-
- Savill J. Apoptosis in resolution of inflammation. J Leukoc Biol. 1997;61:375–380. - PubMed
-
- Serhan CN, Savill J. Resolution of inflammation: the beginning programs the end. Nat Immunol. 2005;6:1191–1197. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

