sRNA154 a newly identified regulator of nitrogen fixation in Methanosarcina mazei strain Gö1
- PMID: 28296572
- PMCID: PMC5785227
- DOI: 10.1080/15476286.2017.1306170
sRNA154 a newly identified regulator of nitrogen fixation in Methanosarcina mazei strain Gö1
Abstract
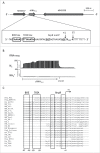
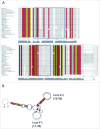
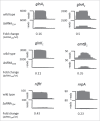
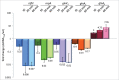
Trans-encoded sRNA154 is exclusively expressed under nitrogen (N)-deficiency in Methanosarcina mazei strain Gö1. The sRNA154 deletion strain showed a significant decrease in growth under N-limitation, pointing toward a regulatory role of sRNA154 in N-metabolism. Aiming to elucidate its regulatory function we characterized sRNA154 by means of biochemical and genetic approaches. 24 homologs of sRNA154 were identified in recently reported draft genomes of Methanosarcina strains, demonstrating high conservation in sequence and predicted secondary structure with two highly conserved single stranded loops. Transcriptome studies of sRNA154 deletion mutants by an RNA-seq approach uncovered nifH- and nrpA-mRNA, encoding the α-subunit of nitrogenase and the transcriptional activator of the nitrogen fixation (nif)-operon, as potential targets besides other components of the N-metabolism. Furthermore, results obtained from stability, complementation and western blot analysis, as well as in silico target predictions combined with electrophoretic mobility shift-assays, argue for a stabilizing effect of sRNA154 on the polycistronic nif-mRNA and nrpA-mRNA by binding with both loops. Further identified N-related targets were studied, which demonstrates that translation initiation of glnA2-mRNA, encoding glutamine synthetase2, appears to be affected by sRNA154 masking the ribosome binding site, whereas glnA1-mRNA appears to be stabilized by sRNA154. Overall, we propose that sRNA154 has a crucial regulatory role in N-metabolism in M. mazei by stabilizing the polycistronic mRNA encoding nitrogenase and glnA1-mRNA, as well as allowing a feed forward regulation of nif-gene expression by stabilizing nrpA-mRNA. Consequently, sRNA154 represents the first archaeal sRNA, for which a positive posttranscriptional regulation is demonstrated as well as inhibition of translation initiation.
Keywords: Methanosarcina mazei; RNA stability; nitrogen fixation; nitrogenase; regulatory RNAs.
Figures


References
-
- Huergo LF, Pedrosa FO, Muller-Santos M, Chubatsu LS, Monteiro RA, Merrick M, Souza EM. PII signal transduction proteins: pivotal players in post-translational control of nitrogenase activity. Microbiology 2012; 158:176-90; PMID:22210804; https://doi.org/10.1099/mic.0.049783-0 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Masepohl B, Hallenbeck PC. Nitrogen and molybdenum control of nitrogen fixation in the phototrophic bacterium Rhodobacter capsulatus. Adv Exp Med Biol 2010; 675:49-70; PMID:20532735; https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-1528-3_4 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dixon R, Kahn D. Genetic regulation of biological nitrogen fixation. Nat Rev Microbiol 2004; 2:621-31; PMID:15263897; https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro954 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dodsworth JA, Leigh JA. Regulation of nitrogenase by 2-oxoglutarate-reversible, direct binding of a PII-like nitrogen sensor protein to dinitrogenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2006; 103:9779-84; PMID:16777963; https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0602278103 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
