Design, methodology, and baseline data of the Personalized Addition Lenses Clinical Trial (PACT)
- PMID: 28296722
- PMCID: PMC5369877
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000006069
Design, methodology, and baseline data of the Personalized Addition Lenses Clinical Trial (PACT)
Abstract
Background: The aim of this study was to describe the design, methods, and baseline characteristics of children enrolled in the Personalized Addition lenses Clinical Trial (PACT). PACT aims to test the myopia control efficacy of progressive addition lenses (PALs) with personalized addition values compared with standard (+2.00 D) addition PALs and single vision lenses (SVLs).
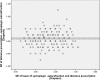
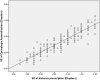
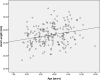
Methods: PACT is a randomized, controlled, double-masked clinical trial. Two hundred eleven myopic Chinese children (7-12 years) were enrolled and randomized into 1 of the 3 following groups: personalized addition PALs; +2.00 addition PALs; and SVLs. Personalized addition values were determined based on the highest addition that satisfied Sheard criterion. Axial length and other biometric data were also recorded.
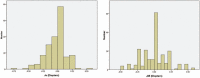
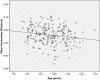
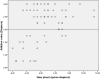
Results: At baseline, no differences were found between the right and left eyes for any of the main parameters. The enrolled children were 9.7 ± 1.1 years' old with cycloplegic autorefraction (right eye [OD]: -2.36 ± 0.64 D), near phoria (1.0 ± 5.0 prism diopter esophoria), lag of accommodation (1.40 ± 0.50 D) and axial length (OD: 24.58 ± 0.74 mm). The personalized addition values ranged from +0.75 to +3.00 (average ± SD: 2.19 ± 0.73 D).
Conclusion: PACT is a clinical trial evaluating whether myopia progression in children can be slowed by wearing personalized addition PALs compared with fixed addition PALs and SVLs as measured by cycloplegic autorefraction and axial length. Baseline data were comparable with those of previous myopia control studies in children. Subjects will be followed up every 6 months for 2 years.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- You QS, Wu LJ, Duan JL, et al. Prevalence of myopia in school children in greater Beijing: the Beijing Childhood Eye Study. Acta Ophthalmol 2014;92:e398–406. - PubMed
-
- Cheng SC, Lam CS, Yap MK. Prevalence of myopia-related retinal changes among 12–18 year old Hong Kong Chinese high myopes. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt 2013;33:652–60. - PubMed
-
- Li X. Beijing Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment Study Group. Incidence and epidemiological characteristics of rhegmatogenous retinal detachment in Beijing, China. Ophthalmology 2003;110:2413–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

