Prognostic nomogram for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma underwent adjuvant transarterial chemoembolization following curative resection
- PMID: 28296727
- PMCID: PMC5369882
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000006140
Prognostic nomogram for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma underwent adjuvant transarterial chemoembolization following curative resection
Abstract
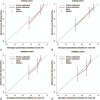
Adjuvant transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) is a major option for postoperative hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients with recurrence risk factors. However, individualized predictive models for subgroup of these patients are limited. This study aimed to develop a prognostic nomogram for patients with HCC underwent adjuvant TACE following curative resection.A cohort comprising 144 HCC patients who received adjuvant TACE following curative resection in the Zhongshan Hospital were analyzed. The nomogram was formulated based on independent prognostic indicators for overall survival (OS). The performance of the nomogram was evaluated by the concordance index (C-index), calibration curve, and decision curve analysis (DCA) and compared with the conventional staging systems. The results were validated in an independent cohort of 86 patients with the same inclusion criteria.Serum alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), hyper-sensitive C-reactive protein (hs-CRP), incomplete tumor encapsulation, and double positive staining of Cytokeratin 7 and Cytokeratin 19 on tumor cells were identified as independent predictors for OS. The C-indices of the nomogram for OS prediction in the training cohort and validation cohort were 0.787 (95%CI 0.775-0.799) and 0.714 (95%CI 0.695-0.733), respectively. In both the training and validation cohorts, the calibration plot showed good consistency between the nomogram-predicted and the observed survival. Furthermore, the established nomogram was superior to the conventional staging systems in terms of C-index and clinical net benefit on DCA.The proposed nomogram provided an accurate prediction on risk stratification for HCC patients underwent adjuvant TACE following curative resection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A nomogram to predict survival of patients with intermediate-stage hepatocellular carcinoma after transarterial chemoembolization combined with microwave ablation.Eur Radiol. 2020 Apr;30(4):2377-2390. doi: 10.1007/s00330-019-06438-8. Epub 2020 Jan 3. Eur Radiol. 2020. PMID: 31900694
-
Development and validation of a novel online calculator for estimating survival benefit of adjuvant transcatheter arterial chemoembolization in patients undergoing surgery for hepatocellular carcinoma.J Hematol Oncol. 2021 Oct 12;14(1):165. doi: 10.1186/s13045-021-01180-5. J Hematol Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34641921 Free PMC article.
-
Transarterial chemoembolization combined with recombinant human adenovirus type 5 H101 prolongs overall survival of patients with intermediate to advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a prognostic nomogram study.Chin J Cancer. 2017 Jul 20;36(1):59. doi: 10.1186/s40880-017-0227-2. Chin J Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28728568 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic nomogram for post-surgical treatment with adjuvant TACE in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma.Oncotarget. 2016 Sep 6;7(36):58302-58314. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11078. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27506942 Free PMC article.
-
Adjuvant therapy following curative treatments for hepatocellular carcinoma: current dilemmas and prospects.Front Oncol. 2023 Apr 17;13:1098958. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1098958. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37139151 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Performance of a Nomogram Based on the Integration of Inflammation Markers with Tumor Staging in Prognosis Prediction of Stage III Colorectal Cancer.Cancer Manag Res. 2020 Aug 7;12:7077-7085. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S263577. eCollection 2020. Cancer Manag Res. 2020. PMID: 32821170 Free PMC article.
-
A simplified model for prophylactic transarterial chemoembolization after resection for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.PLoS One. 2022 Oct 31;17(10):e0276627. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0276627. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36315553 Free PMC article.
-
Nomogram Based on Systemic Immune Inflammation Index and Prognostic Nutrition Index Predicts Recurrence of Hepatocellular Carcinoma After Surgery.Front Oncol. 2020 Oct 14;10:551668. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.551668. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33163397 Free PMC article.
-
The value of intra-procedural transcatheter intraarterial contrast-enhanced ultrasonography (IA-CEUS) in predicting the short-term efficacy of conventional transarterial chemoembolization (cTACE).Transl Cancer Res. 2020 May;9(5):3600-3609. doi: 10.21037/tcr.2020.04.17. Transl Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 35117723 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic Nomograms for Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma After Curative Hepatectomy, with a Focus on Recurrence Timing and Post-Recurrence Management.J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2020 Oct 27;7:233-256. doi: 10.2147/JHC.S271498. eCollection 2020. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2020. PMID: 33154956 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin 2015;65:87–108. - PubMed
-
- Zhong JH, Li LQ. Postoperative adjuvant transarterial chemoembolization for participants with hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis. Hepatol Res 2010;40:943–53. - PubMed
-
- Palmer DH, Midgley RS, Mirza N, et al. A phase II study of adoptive immunotherapy using dendritic cells pulsed with tumor lysate in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2009;49:124–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

