Efficacy of fresh packed red blood transfusion in organophosphate poisoning
- PMID: 28296779
- PMCID: PMC5369934
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000006375
Efficacy of fresh packed red blood transfusion in organophosphate poisoning
Abstract
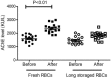
The mortality rate caused by organophosphate (OP) poisoning is still high, even the standard treatment such as atropine and oxime improves a lot. To search for alternative therapies, this study was aimed to investigate the effects of packed red blood cell (RBC) transfusion in acute OP poisoning, and compare the therapeutic effects of RBCs at different storage times.Patients diagnosed with OP poisoning were included in this prospective study. Fresh RBCs (packed RBCs stored less than 10 days) and longer-storage RBCs (stored more than 10 days but less than 35 days) were randomly transfused or not into OP poisoning patients. Cholinesterase (ChE) levels in blood, atropine usage and durations, pralidoxime durations were measured.We found that both fresh and longer-storage RBCs (200-400 mL) significantly increased blood ChE levels 6 hours after transfusion, shortened the duration for ChE recovery and length of hospital stay, and reduced the usage of atropine and pralidoxime. In addition, fresh RBCs demonstrated stronger therapeutic effects than longer-storage RBCs.Packed RBCs might be an alternative approach in patients with OP poisoning, especially during early stages.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Catano HC, Carranza E, Huamani C, et al. Plasma cholinesterase levels and health symptoms in peruvian farm workers exposed to organophosphate pesticides. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 2008;55:153–9. - PubMed
-
- Eddleston M. Patterns and problems of deliberate self-poisoning in the developing world. QJM 2000;93:715–31. - PubMed
-
- Li Y, Tse ML, Gawarammana I, et al. Systematic review of controlled clinical trials of gastric lavage in acute organophosphorus pesticide poisoning. Clin Toxicol (Phila) 2009;47:179–92. - PubMed
-
- Rickett DL, Glenn JF, Beers ET. Central respiratory effects versus neuromuscular actions of nerve agents. Neurotoxicology 1986;7:225–36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous