Differentially expressed miRNAs in sepsis-induced acute kidney injury target oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction pathways
- PMID: 28296904
- PMCID: PMC5351858
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0173292
Differentially expressed miRNAs in sepsis-induced acute kidney injury target oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction pathways
Abstract
Objective: To identify specific miRNAs involved in sepsis-induced AKI and to explore their targeting pathways.
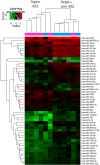
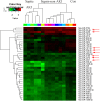
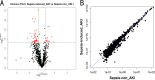
Methods: The expression profiles of miRNAs in serum from patients with sepsis-induced AKI (n = 6), sepsis-non AKI (n = 6), and healthy volunteers (n = 3) were investigated by microarray assay and validated by quantitative PCR (qPCR). The targets of the differentially expressed miRNAs were predicted by Target Scan, mirbase and Miranda. Then the significant functions and involvement in signaling pathways of gene ontology (GO) and KEGG pathways were analyzed. Furthermore, eight miRNAs were randomly selected out of the differentially expressed miRNAs for further testing by qPCR.
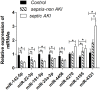
Results: qPCR analysis confirmed that the expressions levels of hsa-miR-23a-3p, hsa-miR-4456, hsa-miR-142-5p, hsa-miR-22-3p and hsa-miR-191-5p were significantly lower in patients with sepsis compared with the healthy volunteers, while hsa-miR-4270, hsa-miR-4321, hsa-miR-3165 were higher in the sepsis patients. Statistically, miR-4321; miR-4270 were significantly upregulated in the sepsis-induced AKI compared with sepsis-non AKI, while only miR-4321 significantly overexpressed in the sepsis groups compared with control groups. GO analysis showed that biological processes regulated by the predicted target genes included diverse terms. They were related to kidney development, regulation of nitrogen compound metabolic process, regulation of cellular metabolic process, cellular response to oxidative stress, mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization, etc. Pathway analysis showed that several significant pathways of the predicted target genes related to oxidative stress. miR-4321 was involved in regulating AKT1, mTOR and NOX5 expression while miR-4270 was involved in regulating PPARGC1A, AKT3, NOX5, PIK3C3, WNT1 expression. Function and pathway analysis highlighted the possible involvement of miRNA-deregulated mRNAs in oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction.
Conclusion: This study might help to improve understanding of the relationship between serum miRNAs and sepsis-induced AKI, and laid an important foundation for further identification of the potential mechanisms of sepsis-induced AKI and oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
The miR-15a-5p-XIST-CUL3 regulatory axis is important for sepsis-induced acute kidney injury.Ren Fail. 2019 Nov;41(1):955-966. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2019.1669460. Ren Fail. 2019. PMID: 31658856 Free PMC article.
-
miRNA-seq analysis of human vertebrae provides insight into the mechanism underlying GIOP.Bone. 2019 Mar;120:371-386. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2018.11.013. Epub 2018 Nov 29. Bone. 2019. PMID: 30503955
-
Serum microRNA array analysis identifies miR-140-3p, miR-33b-3p and miR-671-3p as potential osteoarthritis biomarkers involved in metabolic processes.Clin Epigenetics. 2017 Dec 12;9:127. doi: 10.1186/s13148-017-0428-1. eCollection 2017. Clin Epigenetics. 2017. PMID: 29255496 Free PMC article.
-
Novel findings from determination of common expressed plasma exosomal microRNAs in patients with psoriatic arthritis, psoriasis vulgaris, rheumatoid arthritis, and gouty arthritis.Discov Med. 2019 Jul;28(151):47-68. Discov Med. 2019. PMID: 31465725
-
Noncoding RNAs in acute kidney injury.J Cell Physiol. 2019 Mar;234(3):2266-2276. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27203. Epub 2018 Aug 26. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30146769 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring the Therapeutic Significance of microRNAs and lncRNAs in Kidney Diseases.Genes (Basel). 2024 Jan 19;15(1):123. doi: 10.3390/genes15010123. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38275604 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of miRNA dysregulation in sepsis.Mol Med. 2022 Aug 19;28(1):99. doi: 10.1186/s10020-022-00527-z. Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 35986237 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Discovery and validation of miR-452 as an effective biomarker for acute kidney injury in sepsis.Theranostics. 2020 Oct 25;10(26):11963-11975. doi: 10.7150/thno.50093. eCollection 2020. Theranostics. 2020. PMID: 33204323 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical significance of miR-625-5p in patients with sepsis-induced acute kidney injury based on bioinformatics analysis.Int Urol Nephrol. 2025 Feb;57(2):603-611. doi: 10.1007/s11255-024-04209-z. Epub 2024 Sep 19. Int Urol Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 39294516
-
lncRNA GAS5‑mediated miR‑23a‑3p promotes inflammation and cell apoptosis by targeting TLR4 in a cell model of sepsis.Mol Med Rep. 2021 Jul;24(1):510. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12149. Epub 2021 May 13. Mol Med Rep. 2021. PMID: 33982771 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Keir I, Kellum JA. Acute kidney injury in severe sepsis: pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment recommendations. Journal of veterinary emergency and critical care (San Antonio, Tex: 2001). 2015;25(2):200–9. Epub 2015/04/08. - PubMed
-
- Bagshaw SM, Uchino S, Bellomo R, Morimatsu H, Morgera S, Schetz M, et al. Septic acute kidney injury in critically ill patients: clinical characteristics and outcomes. Clinical journal of the American Society of Nephrology: CJASN. 2007;2(3):431–9. Epub 2007/08/19. 10.2215/CJN.03681106 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

