Co-ingestion of carbohydrate and whey protein increases fasted rates of muscle protein synthesis immediately after resistance exercise in rats
- PMID: 28296942
- PMCID: PMC5351968
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0173809
Co-ingestion of carbohydrate and whey protein increases fasted rates of muscle protein synthesis immediately after resistance exercise in rats
Abstract
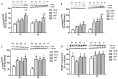
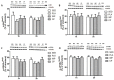
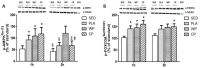
The objective of the study was to investigate whether co-ingestion of carbohydrate and protein as compared with protein alone augments muscle protein synthesis (MPS) during early exercise recovery. Two months old rats performed 10 repetitions of ladder climbing with 75% of body weight attached to their tails. Placebo (PLA), whey protein (WP), or whey protein plus carbohydrate (CP) was then given to rats by gavage. An additional group of sedentary rats (SED) was used as controls. Blood samples were collected immediately and at either 1 or 2 h after exercise. The flexor hallucis longus muscle was excised at 1 or 2 h post exercise for analysis of MPS and related signaling proteins. MPS was significantly increased by CP compared with PLA (p<0.05), and approached significance compared with WP at 1 h post exercise (p = 0.08). CP yielded a greater phosphorylation of mTOR compared with SED and PLA at 1 h post exercise and SED and WP at 2 h post exercise. CP also increased phosphorylation of p70S6K compared with SED at 1 and 2 h post exercise. 4E-BP1 phosphorylation was inhibited by PLA at 1 h but elevated by WP and CP at 2 h post exercise relative to SED. The phosphorylation of AMPK was elevated by exercise at 1 h post exercise, and this elevated level was sustained only in the WP group at 2 h. The phosphorylation of Akt, GSK3, and eIF2Bε were unchanged by treatments. Plasma insulin was transiently increased by CP at 1 h post exercise. In conclusion, post-exercise CP supplementation increases MPS post exercise relative to PLA and possibly WP, which may have been mediated by greater activation of the mTOR signaling pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Phillips SM, Tipton KD, Aarsland A, Wolf SE, Wolfe RR. Mixed muscle protein synthesis and breakdown after resistance exercise in humans. Am J Physiol. 1997;273(1 Pt 1):E99–107. Epub 1997/07/01. - PubMed
-
- Hernandez JM, Fedele MJ, Farrell PA. Time course evaluation of protein synthesis and glucose uptake after acute resistance exercise in rats. J Appl Physiol. 2000;88(3):1142–9. Epub 2000/03/10. - PubMed
-
- Anthony TG, McDaniel BJ, Knoll P, Bunpo P, Paul GL, McNurlan MA. Feeding meals containing soy or whey protein after exercise stimulates protein synthesis and translation initiation in the skeletal muscle of male rats. J Nutr. 2007;137(2):357–62. Epub 2007/01/24. - PubMed
-
- Biolo G, Maggi SP, Williams BD, Tipton KD, Wolfe RR. Increased rates of muscle protein turnover and amino acid transport after resistance exercise in humans. Am J Physiol. 1995;268(3 Pt 1):E514–20. Epub 1995/03/01. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

