In-silico design, expression, and purification of novel chimeric Escherichia coli O157:H7 OmpA fused to LTB protein in Escherichia coli
- PMID: 28296951
- PMCID: PMC5351874
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0173761
In-silico design, expression, and purification of novel chimeric Escherichia coli O157:H7 OmpA fused to LTB protein in Escherichia coli
Abstract
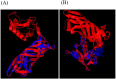
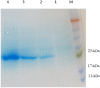
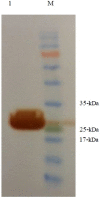
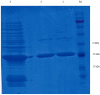
E. coli O157:H7, one of the major EHEC serotypes, is capable of developing bloody diarrhea, hemorrhagic colitis (HC), and fatal hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS) and is accompanied by high annual economic loss worldwide. Due to the increased risk of HC and HUS development following antibiotic therapy, the prevention of infections caused by this pathogen is considered to be one of the most effective ways of avoiding the consequences of this infection. The main aim of the present study was to design, express, and purify a novel chimeric protein to develope human vaccine candidate against E. coli O157:H7 containing loop 2-4 of E. coli O157:H7, outer membrane protein A (OmpA), and B subunit of E. coli heat labile enterotoxin (LTB) which are connected by a flexible peptide linker. Several online databases and bioinformatics software were utilized to choose the peptide linker among 537 analyzed linkers, design the chimeric protein, and optimize the codon of the relative gene encoding this protein. Subsequently, the recombinant gene encoding OmpA-LTB was synthesized and cloned into pET-24a (+) expression vector and transferred to E. coli BL21(DE3) cells. The expression of OmpA-LTB chimeric protein was then carried out by induction of cultured E. coli Bl21 (DE3) cells with 1mM isopropyl-β-D-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG). The purification of OmpA-LTB was then performed by nickel affinity chromatography. Expression and purification were analyzed by sodium dodecyl sulphate poly acrylamide gel electrophoresis. Moreover, the identity of the expressed protein was analyzed by western blotting. SDS-PAGE and western immunoblotting confirmed the successful expression of a 27 KDa recombinant protein after 24 hours at 37°C post-IPTG induction. OmpA-LTB was then successfully purified, using nickel affinity chromatography under denaturing conditions. The yield of purification was 12 mg per liter of culture media. Ultimately, we constructed the successful design and efficient expression and purification of OmpA-LTB divalent under the above-mentioned conditions.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Bardiau M, Gregoire F, Muylaert A, Nahayo A, Duprez JN, Mainil J, et al. Enteropathogenic (EPEC), enterohaemorragic (EHEC) and verotoxigenic (VTEC) Escherichia coli in wild cervids. Journal of applied microbiology. 2010;109(6):2214–22. Epub 2010/10/01. 10.1111/j.1365-2672.2010.04855.x - DOI - PubMed
-
- Manning SD, Motiwala AS, Springman AC, Qi W, Lacher DW, Ouellette LM, et al. Variation in virulence among clades of Escherichia coli O157:H7 associated with disease outbreaks. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2008;105(12):4868–73. Epub 2008/03/12. 10.1073/pnas.0710834105 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sartz L, De Jong B, Hjertqvist M, Plym-Forshell L, Alsterlund R, Lofdahl S, et al. An outbreak of Escherichia coli O157:H7 infection in southern Sweden associated with consumption of fermented sausage; aspects of sausage production that increase the risk of contamination. Epidemiology and infection. 2008;136(3):370–80. Epub 2007/04/21. 10.1017/S0950268807008473 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

