Exome-wide association study reveals novel susceptibility genes to sporadic dilated cardiomyopathy
- PMID: 28296976
- PMCID: PMC5351854
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0172995
Exome-wide association study reveals novel susceptibility genes to sporadic dilated cardiomyopathy
Erratum in
-
Correction: Exome-wide association study reveals novel susceptibility genes to sporadic dilated cardiomyopathy.PLoS One. 2020 Feb 14;15(2):e0229472. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0229472. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32059048 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Aims: Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) is an important cause of heart failure with a strong familial component. We performed an exome-wide array-based association study (EWAS) to assess the contribution of missense variants to sporadic DCM.
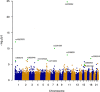
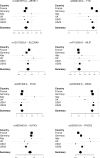
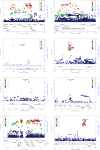
Methods and results: 116,855 single nucleotide variants (SNVs) were analyzed in 2796 DCM patients and 6877 control subjects from 6 populations of European ancestry. We confirmed two previously identified associations with SNVs in BAG3 and ZBTB17 and discovered six novel DCM-associated loci (Q-value<0.01). The lead-SNVs at novel loci are common and located in TTN, SLC39A8, MLIP, FLNC, ALPK3 and FHOD3. In silico fine mapping identified HSPB7 as the most likely candidate at the ZBTB17 locus. Rare variant analysis (MAF<0.01) demonstrated significant association for TTN variants only (P = 0.0085). All candidate genes but one (SLC39A8) exhibit preferential expression in striated muscle tissues and mutations in TTN, BAG3, FLNC and FHOD3 are known to cause familial cardiomyopathy. We also investigated a panel of 48 known cardiomyopathy genes. Collectively, rare (n = 228, P = 0.0033) or common (n = 36, P = 0.019) variants with elevated in silico severity scores were associated with DCM, indicating that the spectrum of genes contributing to sporadic DCM extends beyond those identified here.
Conclusion: We identified eight loci independently associated with sporadic DCM. The functions of the best candidate genes at these loci suggest that proteostasis regulation might play a role in DCM pathophysiology.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Cappola TP, Matkovich SJ, Wang W, van Booven D, Li M, Wang X, et al. Loss-of-function DNA sequence variant in the CLCNKA chloride channel implicates the cardio-renal axis in interindividual heart failure risk variation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108: 2456–2461. 10.1073/pnas.1017494108 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

