Association of Dermatology Consultations With Patient Care Outcomes in Hospitalized Patients With Inflammatory Skin Diseases
- PMID: 28296992
- PMCID: PMC5817615
- DOI: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2016.6130
Association of Dermatology Consultations With Patient Care Outcomes in Hospitalized Patients With Inflammatory Skin Diseases
Abstract
Importance: The value of inpatient dermatology consultations has traditionally been demonstrated with frequency in changes of diagnosis and management; however, the impact of dermatology consultations on metrics such as hospital length of stay and readmission rates remains unknown.
Objective: To determine the association of dermatology consultations with patient care in hospitalized patients using objective values.
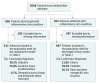
Design, setting, and participants: We retrospectively queried the deidentified database of patients hospitalized between January 1, 2012, and December 31, 2014, at a single university medical center. A total of 413 patients with a primary inflammatory skin condition discharge diagnosis and 647 patients with primary inflammatory skin condition admission diagnosis were selected.
Main outcomes and measures: Hospital length of stay and 1-year readmission with inflammatory skin conditions.
Results: The 413 patients with a primary inflammatory skin condition discharge diagnosis were 61.0% female and had a mean (SD) age of 55.1 (16.4) years. The 647 patients with primary inflammatory skin condition admission diagnosis were 50.8% female and had a mean (SD) age of 57.8 (15.9) years. Multivariable modeling showed that dermatology consultations were associated with a reduction of 1-year inflammatory skin condition readmissions among patients who were discharged primarily with an inflammatory skin condition (readmission probability, 0.0025; 95% CI, 0.00020-0.030 with dermatology consult vs 0.026; 95% CI, 0.0065-0.10 without; odds ratio, 0.093; 95% CI, 0.010-0.840; P = .03). No other confounding variable was associated with reduction in readmissions. Multivariable modeling also showed that dermatology consultations were associated with a reduction in the adjusted hospital length of stay by 2.64 days (95% CI, 1.75-3.53 days; P < .001).
Conclusions and relevance: Dermatology consultations were associated with improvements of outcomes among hospitalized patients. The expansion of the role of dermatology consultation services may improve patient care in a cost-effective manner.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Kirsner RS, Yang DG, Kerdel FA. Dermatologic disease accounts for a large number of hospital admissions annually. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1999;41(6):970-973. - PubMed
-
- Kirsner RS, Yang DG, Kerdel FA. The changing status of inpatient dermatology at American academic dermatology programs. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1999;40(5, pt 1):755-757. - PubMed
-
- Helms AE, Helms SE, Brodell RT. Hospital consultations: time to address an unmet need? J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60(2):308-311. - PubMed
-
- Fox LP, Cotliar J, Hughey L, Kroshinsky D, Shinkai K. Hospitalist dermatology. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;61(1):153-154. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

