Selective Inhibition of ADAM17 Efficiently Mediates Glycoprotein Ibα Retention During Ex Vivo Generation of Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Platelets
- PMID: 28297575
- PMCID: PMC5442763
- DOI: 10.5966/sctm.2016-0104
Selective Inhibition of ADAM17 Efficiently Mediates Glycoprotein Ibα Retention During Ex Vivo Generation of Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Platelets
Abstract
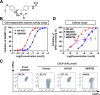
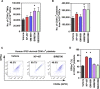
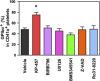
Donor-independent platelet concentrates for transfusion can be produced in vitro from induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs). However, culture at 37°C induces ectodomain shedding on platelets of glycoprotein Ibα (GPIbα), the von Willebrand factor receptor critical for adhesive function and platelet lifetime in vivo, through temperature-dependent activation of a disintegrin and metalloproteinase 17 (ADAM17). The shedding can be suppressed by using inhibitors of panmetalloproteinases and possibly of the upstream regulator p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38 MAPK), but residues of these inhibitors in the final platelet products may be accompanied by harmful risks that prevent clinical application. Here, we optimized the culture conditions for generating human iPSC-derived GPIbα+ platelets, focusing on culture temperature and additives, by comparing a new and safe selective ADAM17 inhibitor, KP-457, with previous inhibitors. Because cultivation at 24°C (at which conventional platelet concentrates are stored) markedly diminished the yield of platelets with high expression of platelet receptors, 37°C was requisite for normal platelet production from iPSCs. KP-457 blocked GPIbα shedding from iPSC platelets at a lower half-maximal inhibitory concentration than panmetalloproteinase inhibitor GM-6001, whereas p38 MAPK inhibitors did not. iPSC platelets generated in the presence of KP-457 exhibited improved GPIbα-dependent aggregation not inferior to human fresh platelets. A thrombus formation model using immunodeficient mice after platelet transfusion revealed that iPSC platelets generated with KP-457 exerted better hemostatic function in vivo. Our findings suggest that KP-457, unlike GM-6001 or p38 MAPK inhibitors, effectively enhances the production of functional human iPSC-derived platelets at 37°C, which is an important step toward their clinical application. Stem Cells Translational Medicine 2017;6:720-730.
Keywords: Cell culture; Cell transplantation; Induced pluripotent stem cell; Megakaryocyte; Mitogen-activated protein kinase; Thrombopoiesis.
© 2016 The Authors Stem Cells Translational Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of AlphaMed Press.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha-converting enzyme (ADAM17) mediates GPIbalpha shedding from platelets in vitro and in vivo.Circ Res. 2004 Oct 1;95(7):677-83. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000143899.73453.11. Epub 2004 Sep 2. Circ Res. 2004. PMID: 15345652
-
Inhibiting GPIbα Shedding Preserves Post-Transfusion Recovery and Hemostatic Function of Platelets After Prolonged Storage.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2016 Sep;36(9):1821-8. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.116.307639. Epub 2016 Jul 14. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2016. PMID: 27417583 Free PMC article.
-
Prolonged inhibition of protein kinase A results in metalloproteinase-dependent platelet GPIbalpha shedding.Thromb Res. 2009 May;124(1):101-9. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2008.12.044. Epub 2009 Jan 31. Thromb Res. 2009. PMID: 19181367
-
[Ex vivo platelet production from induced pluripotent stem cells].Rinsho Ketsueki. 2018;59(10):1905-1913. doi: 10.11406/rinketsu.59.1905. Rinsho Ketsueki. 2018. PMID: 30305491 Review. Japanese.
-
Platelet production from induced pluripotent stem cells.J Thromb Haemost. 2017 Sep;15(9):1717-1727. doi: 10.1111/jth.13736. Epub 2017 Jul 28. J Thromb Haemost. 2017. PMID: 28752663 Review.
Cited by
-
Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Megakaryocytes and Platelets for Disease Modeling and Future Clinical Applications.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017 Nov;37(11):2007-2013. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.117.309197. Epub 2017 Oct 5. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017. PMID: 28982668 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived platelets loaded with lapatinib effectively target HER2+ breast cancer metastasis to the brain.Sci Rep. 2021 Oct 15;11(1):16866. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-96351-2. Sci Rep. 2021. Retraction in: Sci Rep. 2024 Mar 12;14(1):5972. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-56291-z. PMID: 34654856 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Recent Advances in ADAM17 Research: A Promising Target for Cancer and Inflammation.Mediators Inflamm. 2017;2017:9673537. doi: 10.1155/2017/9673537. Epub 2017 Nov 2. Mediators Inflamm. 2017. PMID: 29230082 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Suppressive effects of anagrelide on cell cycle progression and the maturation of megakaryocyte progenitor cell lines in human induced pluripotent stem cells.Haematologica. 2020 May;105(5):e216-e220. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2018.214841. Epub 2019 Sep 5. Haematologica. 2020. PMID: 31488559 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The Effect of Megakaryocytes and Platelets Derived from Human-Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells on Bone Formation.Spine Surg Relat Res. 2021 Feb 22;5(3):196-204. doi: 10.22603/ssrr.2020-0226. eCollection 2021. Spine Surg Relat Res. 2021. PMID: 34179558 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Takahashi K, Tanabe K, Ohnuki M et al. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from adult human fibroblasts by defined factors. Cell 2007;131:861–872. - PubMed
-
- Takayama N, Nishikii H, Usui J et al. Generation of functional platelets from human embryonic stem cells in vitro via ES‐sacs, VEGF‐promoted structures that concentrate hematopoietic progenitors. Blood 2008;111:5298–5306. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

