Endothelial Cells Promote Expansion of Long-Term Engrafting Marrow Hematopoietic Stem and Progenitor Cells in Primates
- PMID: 28297579
- PMCID: PMC5442761
- DOI: 10.5966/sctm.2016-0240
Endothelial Cells Promote Expansion of Long-Term Engrafting Marrow Hematopoietic Stem and Progenitor Cells in Primates
Abstract
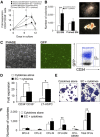
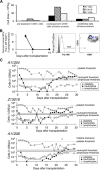
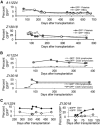
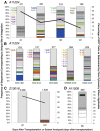
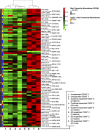
Successful expansion of bone marrow (BM) hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs) would benefit many HSPC transplantation and gene therapy/editing applications. However, current expansion technologies have been limited by a loss of multipotency and self-renewal properties ex vivo. We hypothesized that an ex vivo vascular niche would provide prohematopoietic signals to expand HSPCs while maintaining multipotency and self-renewal. To test this hypothesis, BM autologous CD34+ cells were expanded in endothelial cell (EC) coculture and transplanted in nonhuman primates. CD34+ C38- HSPCs cocultured with ECs expanded up to 17-fold, with a significant increase in hematopoietic colony-forming activity compared with cells cultured with cytokines alone (colony-forming unit-granulocyte-erythroid-macrophage-monocyte; p < .005). BM CD34+ cells that were transduced with green fluorescent protein lentivirus vector and expanded on ECs engrafted long term with multilineage polyclonal reconstitution. Gene marking was observed in granulocytes, lymphocytes, platelets, and erythrocytes. Whole transcriptome analysis indicated that EC coculture altered the expression profile of 75 genes in the BM CD34+ cells without impeding the long-term engraftment potential. These findings show that an ex vivo vascular niche is an effective platform for expansion of adult BM HSPCs. Stem Cells Translational Medicine 2017;6:864-876.
Keywords: Bone marrow transplantation; CD34+ cells; Endothelial cells; Gene therapy; Hematopoietic stem progenitor cell.
© 2016 The Authors Stem Cells Translational Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of AlphaMed Press.
Figures

References
-
- Anguita‐Compagnon AT, Dibarrart MT, Palma J et al. Mobilization and collection of peripheral blood stem cells: Guidelines for blood volume to process, based on CD34‐positive blood cell count in adults and children. Transplant Proc 2010;42:339–344. - PubMed
-
- Perseghin P, Terruzzi E, Dassi M et al. Management of poor peripheral blood stem cell mobilization: Incidence, predictive factors, alternative strategies and outcome. A retrospective analysis on 2177 patients from three major Italian institutions. Transfus Apheresis Sci 2009;41:33–37. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

