RNA m6A methylation regulates the ultraviolet-induced DNA damage response
- PMID: 28297716
- PMCID: PMC5490984
- DOI: 10.1038/nature21671
RNA m6A methylation regulates the ultraviolet-induced DNA damage response
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: RNA m6A methylation regulates the ultraviolet-induced DNA damage response.Nature. 2017 Dec 21;552(7685):430. doi: 10.1038/nature24007. Epub 2017 Nov 29. Nature. 2017. PMID: 29186122
Abstract
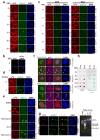
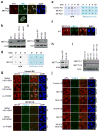
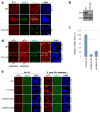
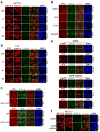
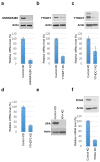
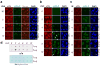
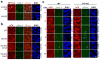
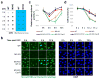
Cell proliferation and survival require the faithful maintenance and propagation of genetic information, which are threatened by the ubiquitous sources of DNA damage present intracellularly and in the external environment. A system of DNA repair, called the DNA damage response, detects and repairs damaged DNA and prevents cell division until the repair is complete. Here we report that methylation at the 6 position of adenosine (m6A) in RNA is rapidly (within 2 min) and transiently induced at DNA damage sites in response to ultraviolet irradiation. This modification occurs on numerous poly(A)+ transcripts and is regulated by the methyltransferase METTL3 (methyltransferase-like 3) and the demethylase FTO (fat mass and obesity-associated protein). In the absence of METTL3 catalytic activity, cells showed delayed repair of ultraviolet-induced cyclobutane pyrimidine adducts and elevated sensitivity to ultraviolet, demonstrating the importance of m6A in the ultraviolet-responsive DNA damage response. Multiple DNA polymerases are involved in the ultraviolet response, some of which resynthesize DNA after the lesion has been excised by the nucleotide excision repair pathway, while others participate in trans-lesion synthesis to allow replication past damaged lesions in S phase. DNA polymerase κ (Pol κ), which has been implicated in both nucleotide excision repair and trans-lesion synthesis, required the catalytic activity of METTL3 for immediate localization to ultraviolet-induced DNA damage sites. Importantly, Pol κ overexpression qualitatively suppressed the cyclobutane pyrimidine removal defect associated with METTL3 loss. Thus, we have uncovered a novel function for RNA m6A modification in the ultraviolet-induced DNA damage response, and our findings collectively support a model in which m6A RNA serves as a beacon for the selective, rapid recruitment of Pol κ to damage sites to facilitate repair and cell survival.
Conflict of interest statement
Y.S. is a cofounder of Constellation Pharmaceuticals and a member of its scientific advisory board, and a consultant for Active Motif, Inc.
Figures

Similar articles
-
FTO suppresses DNA repair by inhibiting PARP1.Nat Commun. 2025 Mar 25;16(1):2925. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-58309-0. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40133293 Free PMC article.
-
Requirement for functional DNA polymerase eta in genome-wide repair of UV-induced DNA damage during S phase.DNA Repair (Amst). 2010 Jul 1;9(7):754-64. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2010.03.013. Epub 2010 Apr 24. DNA Repair (Amst). 2010. PMID: 20457011
-
Predominant role of DNA polymerase eta and p53-dependent translesion synthesis in the survival of ultraviolet-irradiated human cells.Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Feb 17;45(3):1270-1280. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw1196. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 28180309 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Dynamic m6 A RNA Methylation in Photobiology.Photochem Photobiol. 2019 Jan;95(1):95-104. doi: 10.1111/php.12930. Epub 2018 May 24. Photochem Photobiol. 2019. PMID: 29729018 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA polymerases and repair synthesis in NER in human cells.DNA Repair (Amst). 2011 Jul 15;10(7):730-3. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2011.04.023. Epub 2011 May 20. DNA Repair (Amst). 2011. PMID: 21601536 Review.
Cited by
-
RBM15 facilitates laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma progression by regulating TMBIM6 stability through IGF2BP3 dependent.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021 Feb 26;40(1):80. doi: 10.1186/s13046-021-01871-4. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 33637103 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophil extracellular traps-triggered impaired autophagic flux via METTL3 underlies sepsis-associated acute lung injury.Cell Death Discov. 2022 Aug 27;8(1):375. doi: 10.1038/s41420-022-01166-3. Cell Death Discov. 2022. PMID: 36030287 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory Role of N6-methyladenosine (m6A) Modification in Osteosarcoma.Front Oncol. 2021 May 19;11:683768. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.683768. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34094986 Free PMC article. Review.
-
METTL14 affects UVB-induced human dermal fibroblasts photoaging via miR-100-3p biogenesis in an m6A-dependent manner.Aging Cell. 2024 May;23(5):e14123. doi: 10.1111/acel.14123. Epub 2024 Feb 21. Aging Cell. 2024. PMID: 38380598 Free PMC article.
-
Context-Dependent Roles of RNA Modifications in Stress Responses and Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 16;22(4):1949. doi: 10.3390/ijms22041949. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33669361 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

