Association of mannose-binding lectin gene polymorphisms with the development of pulmonary tuberculosis in China
- PMID: 28298186
- PMCID: PMC5353790
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-017-2310-3
Association of mannose-binding lectin gene polymorphisms with the development of pulmonary tuberculosis in China
Abstract
Background: Mannose-binding lectin (MBL) is an important protein in the lectin pathway of the immune system. This study explores the association between MBL polymorphism and the susceptibility to tuberculosis (TB). The association between the MBL2 polymorphisms and serum MBL levels is also analyzed in the present study.
Methods: A total of 112 inpatients with pulmonary TB and 120 healthy controls were recruited to participate in this case-control study. Polymerase Chain Reaction-Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism(PCR-RFLP) technology was used to genotype MBL gene (variants in -221Y/X and exon l codons 54 A/B). Serum MBL level was assayed by human MBL ELISA kit. Demographic data and exposure information were also obtained from the study participants.
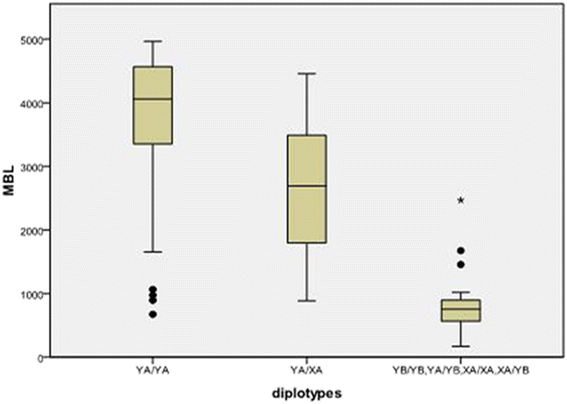
Results: Genotypes YA/YA of MBL gene were more prevalent in the healthy control group than in the TB patient (P =0.038, OR, 0.57; 95% CI, 0.34-0.97) and genotypes XA/XA were less frequent in the healthy control group (P =0.007, OR, 6.42; 95% CI, 1.39-29.67). The resistant diplotype was more frequently found in the younger patients and retreatment cases with TB in MBL gene sites -221Y/X or codon 54 A/B. X/Y and A/B polymorphisms were strong determinants of serum MBL levels.
Conclusion: The polymorphisms of MBL gene may be associated with susceptibility to TB and the recurrence of TB. The YA/YA may be a protected diplotype against TB.
Keywords: Mannose-binding lectin (MBL); Polymorphism; Susceptibility; Tuberculosis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mannose binding lectin gene variants and susceptibility to tuberculosis in HIV-1 infected patients of South India.Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2007 Nov;87(6):535-43. doi: 10.1016/j.tube.2007.07.007. Epub 2007 Sep 12. Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2007. PMID: 17855170
-
Age-dependent association of mannose-binding lectin polymorphisms with the development of pulmonary tuberculosis in Viet Nam.Hum Immunol. 2014 Aug;75(8):840-6. doi: 10.1016/j.humimm.2014.06.006. Epub 2014 Jun 19. Hum Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24952212
-
Mannose-binding lectin exon 1 and promoter polymorphisms in tuberculosis disease in a Mediterranean area.Int J Immunogenet. 2014 Aug;41(4):306-11. doi: 10.1111/iji.12126. Epub 2014 Jun 9. Int J Immunogenet. 2014. PMID: 24910008
-
Mannose-binding lectin and susceptibility to tuberculosis: a meta-analysis.Clin Exp Immunol. 2010 Oct;162(1):84-90. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2010.04221.x. Epub 2010 Aug 19. Clin Exp Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20636396 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association between the mannose-binding lectin (MBL)-2 gene variants and serum MBL with pulmonary tuberculosis: An update meta-analysis and systematic review.Microb Pathog. 2019 Jul;132:374-380. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2019.04.023. Epub 2019 Apr 15. Microb Pathog. 2019. PMID: 30999018
Cited by
-
Intelectin 3 is dispensable for resistance against a mycobacterial infection in zebrafish (Danio rerio).Sci Rep. 2019 Jan 30;9(1):995. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-37678-1. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30700796 Free PMC article.
-
Role of pattern recognition receptors in sensing Mycobacterium tuberculosis.Heliyon. 2023 Oct 4;9(10):e20636. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e20636. eCollection 2023 Oct. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37842564 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association between IFNGR1 gene polymorphisms and tuberculosis susceptibility: A meta-analysis.Front Public Health. 2022 Sep 6;10:976221. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.976221. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36148347 Free PMC article.
-
Mannose-binding lectin gene sequence data in Kelantan population.Sci Data. 2024 Apr 30;11(1):435. doi: 10.1038/s41597-024-03274-4. Sci Data. 2024. PMID: 38688916 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Mannose-Binding Lectin 2 Gene Polymorphism with Tuberculosis Based on Mycobacterium tuberculosis Lineages.Infect Drug Resist. 2022 Mar 24;15:1225-1234. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S344935. eCollection 2022. Infect Drug Resist. 2022. PMID: 35355619 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO . Multidrug and extensively drug-resistant TB (M/XDRTB):2010 global report on surveillance and response. WHO/HTM/TB/2010.3. Geneva: WHO Press; 2010.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

