Erratum to: Association between routine laboratory tests and long-term mortality among acutely admitted older medical patients: a cohort study
- PMID: 28298200
- PMCID: PMC5353888
- DOI: 10.1186/s12877-017-0463-y
Erratum to: Association between routine laboratory tests and long-term mortality among acutely admitted older medical patients: a cohort study
Figures
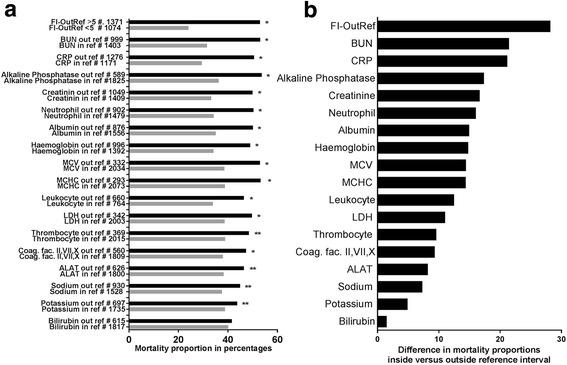
Erratum for
-
Association between routine laboratory tests and long-term mortality among acutely admitted older medical patients: a cohort study.BMC Geriatr. 2017 Mar 1;17(1):62. doi: 10.1186/s12877-017-0434-3. BMC Geriatr. 2017. PMID: 28249621 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

