Chidamide in relapsed or refractory peripheral T cell lymphoma: a multicenter real-world study in China
- PMID: 28298231
- PMCID: PMC5351273
- DOI: 10.1186/s13045-017-0439-6
Chidamide in relapsed or refractory peripheral T cell lymphoma: a multicenter real-world study in China
Abstract
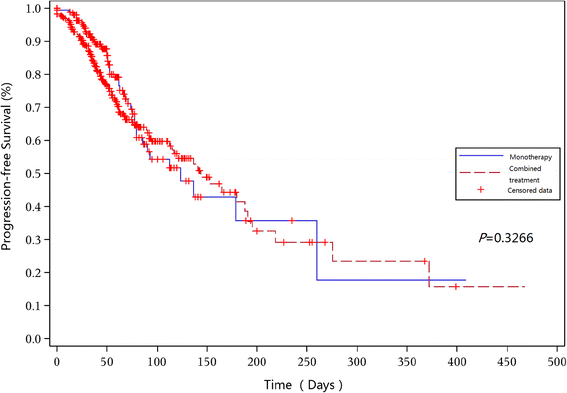
The efficacy and safety of chidamide, a new subtype-selective histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor, have been demonstrated in a pivotal phase II clinical trial, and chidamide has been approved by the China Food and Drug Administration (CFDA) as a treatment for relapsed or refractory peripheral T cell lymphoma (PTCL). This study sought to further evaluate the real-world utilization of chidamide in 383 relapsed or refractory PTCL patients from April 2015 to February 2016 in mainland China. For patients receiving chidamide monotherapy (n = 256), the overall response rate (ORR) and disease control rate (DCR) were 39.06 and 64.45%, respectively. The ORR and DCR were 51.18 and 74.02%, respectively, for patients receiving chidamide combined with chemotherapy (n = 127). For patients receiving chidamide monotherapy and chidamide combined with chemotherapy, the median progression-free survival (PFS) was 129 (95% CI 82 to 194) days for the monotherapy group and 152 (95% CI 93 to 201) days for the combined therapy group (P = 0.3266). Most adverse events (AEs) were of grade 1 to 2. AEs of grade 3 or higher that occurred in ≥5% of patients receiving chidamide monotherapy included thrombocytopenia (10.2%) and neutropenia (6.2%). For patients receiving chidamide combined with chemotherapy, grade 3 to 4 AEs that occurred in ≥5% of patients included thrombocytopenia (18.1%), neutropenia (12.6%), anemia (7.1%), and fatigue (5.5%). This large real-world study demonstrates that chidamide has a favorable efficacy and an acceptable safety profile for refractory and relapsed PTCL patients. Chidamide combined with chemotherapy may be a new treatment choice for refractory and relapsed PTCL patients but requires further investigation.
Keywords: Chemotherapy; Chidamide; Peripheral T cell lymphoma; Treatment.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous