AMPA receptor-mediated rapid EPSCs in vestibular calyx afferents
- PMID: 28298303
- PMCID: PMC5491709
- DOI: 10.1152/jn.00394.2016
AMPA receptor-mediated rapid EPSCs in vestibular calyx afferents
Abstract
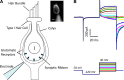
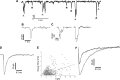
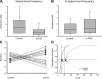
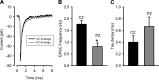
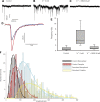
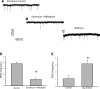
In the vestibular periphery neurotransmission between hair cells and primary afferent nerves occurs via specialized ribbon synapses. Type I vestibular hair cells (HCIs) make synaptic contacts with calyx terminals, which enclose most of the HCI basolateral surface. To probe synaptic transmission, whole cell patch-clamp recordings were made from calyx afferent terminals isolated together with their mature HCIs from gerbil crista. Neurotransmitter release was measured as excitatory postsynaptic currents (EPSCs) in voltage clamp. Spontaneous EPSCs were classified as simple or complex. Simple events exhibited a rapid rise time and a fast monoexponential decay (time constant < 1 ms). The remaining events, constituting ~40% of EPSCs, showed more complex characteristics. Extracellular Sr2+ greatly increased EPSC frequency, and EPSCs were blocked by the AMPA receptor blocker NBQX. The role of presynaptic Ca2+ channels was assessed by application of the L-type Ca2+ channel blocker nifedipine (20 µM), which reduced EPSC frequency. In contrast, the L-type Ca2+ channel opener BAY K 8644 increased EPSC frequency. Cyclothiazide increased the decay time constant of averaged simple EPSCs by approximately twofold. The low-affinity AMPA receptor antagonist γ-d-glutamylglycine (2 mM) reduced the proportion of simple EPSCs relative to complex events, indicating glutamate accumulation in the restricted cleft between HCI and calyx. In crista slices EPSC frequency was greater in central compared with peripheral calyces, which may be due to greater numbers of presynaptic ribbons in central hair cells. Our data support a role for L-type Ca2+ channels in spontaneous release and demonstrate regional variations in AMPA-mediated quantal transmission at the calyx synapse.NEW & NOTEWORTHY In vestibular calyx terminals of mature cristae we find that the majority of excitatory postsynaptic currents (EPSCs) are rapid monophasic events mediated by AMPA receptors. Spontaneous EPSCs are reduced by an L-type Ca2+ channel blocker and notably enhanced in extracellular Sr2+ EPSC frequency is greater in central areas of the crista compared with peripheral areas and may be associated with more numerous presynaptic ribbons in central hair cells.
Keywords: AMPA receptor; crista; cyclothiazide; glutamate; type I hair cell.
Copyright © 2017 the American Physiological Society.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Glutamatergic signaling at the vestibular hair cell calyx synapse.J Neurosci. 2014 Oct 29;34(44):14536-50. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0369-13.2014. J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25355208 Free PMC article.
-
Prolonged physiological entrapment of glutamate in the synaptic cleft of cerebellar unipolar brush cells.J Neurophysiol. 1997 Sep;78(3):1320-33. doi: 10.1152/jn.1997.78.3.1320. J Neurophysiol. 1997. PMID: 9310423
-
Persistent and resurgent Na+ currents in vestibular calyx afferents.J Neurophysiol. 2020 Aug 1;124(2):510-524. doi: 10.1152/jn.00124.2020. Epub 2020 Jul 15. J Neurophysiol. 2020. PMID: 32667253 Free PMC article.
-
AMPA-type glutamate receptors--nonselective cation channels mediating fast excitatory transmission in the CNS.EXS. 1993;66:61-76. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0348-7327-7_4. EXS. 1993. PMID: 7505664 Review.
-
Simultaneous Dual Recordings From Vestibular Hair Cells and Their Calyx Afferents Demonstrate Multiple Modes of Transmission at These Specialized Endings.Front Neurol. 2022 Jul 11;13:891536. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.891536. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35899268 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Increased Type I and Decreased Type II Hair Cells after Deletion of Sox2 in the Developing Mouse Utricle.Neuroscience. 2019 Dec 1;422:146-160. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2019.09.027. Epub 2019 Oct 31. Neuroscience. 2019. PMID: 31678344 Free PMC article.
-
Direct current effects on afferent and hair cell to elicit natural firing patterns.iScience. 2021 Feb 20;24(3):102205. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.102205. eCollection 2021 Mar 19. iScience. 2021. PMID: 33748701 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of hyperpolarization-activated current (Ih) in zonally defined vestibular calyx terminals of the crista.J Neurophysiol. 2023 Jun 1;129(6):1468-1481. doi: 10.1152/jn.00135.2023. Epub 2023 May 17. J Neurophysiol. 2023. PMID: 37198134 Free PMC article.
-
Conditional deletion of Neurexin-2 alters neuronal network activity in hippocampal circuitries and leads to spontaneous seizures.Transl Psychiatry. 2023 Mar 20;13(1):97. doi: 10.1038/s41398-023-02394-6. Transl Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 36941261 Free PMC article.
-
Exocytosis in mouse vestibular Type II hair cells shows a high-order Ca2+ dependence that is independent of synaptotagmin-4.Physiol Rep. 2020 Jul;8(14):e14509. doi: 10.14814/phy2.14509. Physiol Rep. 2020. PMID: 32691536 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

