Ubiquitin E3 ligase Itch negatively regulates osteoblast function by promoting proteasome degradation of osteogenic proteins
- PMID: 28298321
- PMCID: PMC5376659
- DOI: 10.1302/2046-3758.63.BJR-2016-0237.R1
Ubiquitin E3 ligase Itch negatively regulates osteoblast function by promoting proteasome degradation of osteogenic proteins
Abstract
Objectives: Ubiquitin E3 ligase-mediated protein degradation regulates osteoblast function. Itch, an E3 ligase, affects numerous cell functions by regulating ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of related proteins. However, the Itch-related cellular and molecular mechanisms by which osteoblast differentiation and function are elevated during bone fracture repair are as yet unknown.
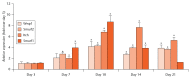
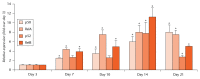
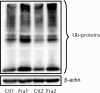
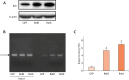
Methods: We examined the expression levels of E3 ligases and NF-κB members in callus samples during bone fracture repair by quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) and the total amount of ubiquitinated proteins by Western blot analysis in wild-type (WT) mice. The expression levels of osteoblast-associated genes in fracture callus from Itch knockout (KO) mice and their WT littermates were examined by qPCR. The effect of NF-κB on Itch expression in C2C12 osteoblast cells was determined by a chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assay.
Results: The expression levels of WW Domain Containing E3 Ubiquitin Protein Ligase 1 (Wwp1), SMAD Specific E3 Ubiquitin Protein Ligase 1 (Smurf1), SMAD Specific E3 Ubiquitin Protein Ligase 2 (Smurf2) and Itch were all significantly increased in the fracture callus of WT mice, which was associated with elevated expression of NF-κB members and total ubiquitinated proteins. Callus tissue isolated from Itch KO mice expressed higher levels of osteoblast-associated genes, including Runx2, a positive regulator of osteoblast differentiation, but osteoclast-associated genes were not increased. Both NF-κB RelA and RelB proteins were found to bind to the NF-κB binding site in the mouse Itch promoter.
Conclusions: Our findings indicate that Itch depletion may have a strong positive effect on osteoblast differentiation in fracture callus. Thus, ubiquitin E3 ligase Itch could be a potential target for enhancing bone fracture healing.Cite this article: J. Liu, X. Li, H. Zhang, R. Gu, Z. Wang, Z. Gao, L. Xing. Ubiquitin E3 ligase Itch negatively regulates osteoblast function by promoting proteasome degradation of osteogenic proteins. Bone Joint Res 2017;6:154-161. DOI: 10.1302/2046-3758.63.BJR-2016-0237.R1.
Keywords: Bone formation; E3 ligase; Fracture; Itch; Osteoblasts.
© 2017 Xing et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ubiquitin E3 ligase Wwp1 negatively regulates osteoblast function by inhibiting osteoblast differentiation and migration.J Bone Miner Res. 2013 Sep;28(9):1925-35. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.1938. J Bone Miner Res. 2013. PMID: 23553732 Free PMC article.
-
Ubiquitin e3 ligase itch negatively regulates osteoblast differentiation from mesenchymal progenitor cells.Stem Cells. 2013 Aug;31(8):1574-83. doi: 10.1002/stem.1395. Stem Cells. 2013. PMID: 23606569 Free PMC article.
-
E3 ubiquitin ligase Smurf1 mediates core-binding factor alpha1/Runx2 degradation and plays a specific role in osteoblast differentiation.J Biol Chem. 2003 Jul 25;278(30):27939-44. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M304132200. Epub 2003 May 7. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12738770
-
E3 Ubiquitin Ligase-Mediated Regulation of Osteoblast Differentiation and Bone Formation.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Aug 27;9:706395. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.706395. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34513836 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulatory Roles of E3 Ubiquitin Ligases and Deubiquitinases in Bone.Biomolecules. 2025 May 7;15(5):679. doi: 10.3390/biom15050679. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40427572 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ubiquitin modification in osteogenic differentiation and bone formation: From mechanisms to clinical significance.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Oct 21;10:1033223. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.1033223. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36340031 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression of Musashi-1 Increases in Bone Healing.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 26;22(7):3395. doi: 10.3390/ijms22073395. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33810326 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome analysis of osteoblasts in an ovariectomized mouse model in response to physical exercise.Bone Joint Res. 2018 Dec 1;7(11):601-608. doi: 10.1302/2046-3758.711.BJR-2018-0075.R2. eCollection 2018 Nov. Bone Joint Res. 2018. PMID: 30581558 Free PMC article.
-
E3 ubiquitin ligases: key regulators of osteogenesis and potential therapeutic targets for bone disorders.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Aug 15;12:1447093. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1447093. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 39211390 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The E3 protein ubiquitin ligase Itch is a potential target in myeloid malignancies with marrow fibrosis.Transl Cancer Res. 2021 May;10(5):2368-2378. doi: 10.21037/tcr-20-3115. Transl Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 35116552 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rotin D, Kumar S. Physiological functions of the HECT family of ubiquitin ligases. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2009;10:398-409. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

