Selective export of autotaxin from the endoplasmic reticulum
- PMID: 28298439
- PMCID: PMC5409469
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M116.774356
Selective export of autotaxin from the endoplasmic reticulum
Abstract
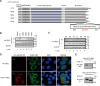
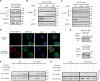
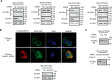
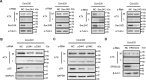
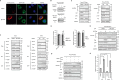
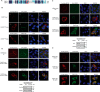
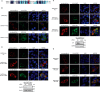
Autotaxin (ATX) or ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase 2 (ENPP2) is a secretory glycoprotein and functions as the key enzyme for lysophosphatidic acid generation. The mechanism of ATX protein trafficking is largely unknown. Here, we demonstrated that p23, a member of the p24 protein family, was the protein-sorting receptor required for endoplasmic reticulum (ER) export of ATX. A di-phenylalanine (Phe-838/Phe-839) motif in the human ATX C-terminal region was identified as a transport signal essential for the ATX-p23 interaction. Knockdown of individual Sec24 isoforms by siRNA revealed that ER export of ATX was impaired only if Sec24C was down-regulated. These results suggest that ATX is selectively exported from the ER through a p23, Sec24C-dependent pathway. In addition, it was found that AKT signaling played a role in ATX secretion regulation to facilitate ATX ER export by enhancing the nuclear factor of activated T cell-mediated p23 expression. Furthermore, the di-hydrophobic amino acid motifs (FY) also existed in the C-terminal regions of human ENPP1 and ENPP3. Such a p23, Sec24C-dependent selective ER export mechanism is conserved among these ENPP family members.
Keywords: COPII; ENPP family; ER export; Sec24C; autotaxin; endoplasmic reticulum (ER); lysophospholipid; p23; protein sorting; receptor.
© 2017 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures
References
-
- Pua T. L., Wang F. Q., and Fishman D. A. (2009) Roles of LPA in ovarian cancer development and progression. Future Oncol. 5, 1659–1673 - PubMed
-
- Willier S., Butt E., and Grunewald T. G. (2013) Lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) signalling in cell migration and cancer invasion: a focussed review and analysis of LPA receptor gene expression on the basis of more than 1700 cancer microarrays. Biol. Cell 105, 317–333 - PubMed
-
- Zaslavsky A., Singh L. S., Tan H., Ding H., Liang Z., and Xu Y. (2006) Homo- and hetero-dimerization of LPA/S1P receptors, OGR1 and GPR4. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1761, 1200–1212 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

