Protein arginine methyltransferases interact with intraflagellar transport particles and change location during flagellar growth and resorption
- PMID: 28298486
- PMCID: PMC5415017
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E16-11-0774
Protein arginine methyltransferases interact with intraflagellar transport particles and change location during flagellar growth and resorption
Abstract
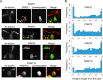
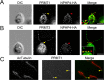
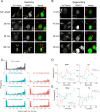
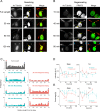
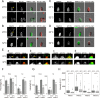
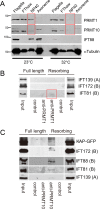
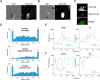
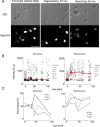
Changes in protein by posttranslational modifications comprise an important mechanism for the control of many cellular processes. Several flagellar proteins are methylated on arginine residues during flagellar resorption; however, the function is not understood. To learn more about the role of protein methylation during flagellar dynamics, we focused on protein arginine methyltransferases (PRMTs) 1, 3, 5, and 10. These PRMTs localize to the tip of flagella and in a punctate pattern along the length, very similar, but not identical, to that of intraflagellar transport (IFT) components. In addition, we found that PRMT 1 and 3 are also highly enriched at the base of the flagella, and the basal localization of these PRMTs changes during flagellar regeneration and resorption. Proteins with methyl arginine residues are also enriched at the tip and base of flagella, and their localization also changes during flagellar assembly and disassembly. PRMTs are lost from the flagella of fla10-1 cells, which carry a temperature-sensitive mutation in the anterograde motor for IFT. The data define the distribution of specific PRMTs and their target proteins in flagella and demonstrate that PRMTs are cargo for translocation within flagella by the process of IFT.
© 2017 Mizuno and Sloboda. This article is distributed by The American Society for Cell Biology under license from the author(s). Two months after publication it is available to the public under an Attribution–Noncommercial–Share Alike 3.0 Unported Creative Commons License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0).
Figures

References
-
- Abramoff MD, Magalhaes PJ, Ram SJ. Image processing with Image J. Biophoton Int. 2004;11:36–42.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

