Macrocycles as protein-protein interaction inhibitors
- PMID: 28298556
- PMCID: PMC6511976
- DOI: 10.1042/BCJ20160619
Macrocycles as protein-protein interaction inhibitors
Abstract
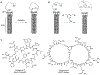
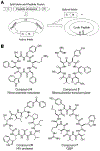
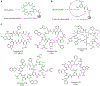
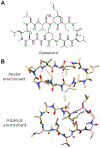
Macrocyclic compounds such as cyclic peptides have emerged as a new and exciting class of drug candidates for inhibition of intracellular protein-protein interactions, which are challenging targets for conventional drug modalities (i.e. small molecules and proteins). Over the past decade, several complementary technologies have been developed to synthesize macrocycle libraries and screen them for binding to therapeutically relevant targets. Two different approaches have also been explored to increase the membrane permeability of cyclic peptides. In this review, we discuss these methods and their applications in the discovery of macrocyclic compounds against protein-protein interactions.
Keywords: cell-penetrating peptide; cyclic peptide; drug discovery; macrocycle; protein–protein interaction; undruggable targets.
© 2017 The Author(s); published by Portland Press Limited on behalf of the Biochemical Society.
Figures


Similar articles
-
SICLOPPS cyclic peptide libraries in drug discovery.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2017 Jun;38:30-35. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2017.02.016. Epub 2017 Mar 1. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2017. PMID: 28258013 Review.
-
Structure-Based Design of Non-natural Macrocyclic Peptides That Inhibit Protein-Protein Interactions.J Med Chem. 2017 Nov 9;60(21):8982-8988. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.7b01221. Epub 2017 Oct 27. J Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 29028171 Free PMC article.
-
Bicyclic Peptides as Next-Generation Therapeutics.Chemistry. 2017 Sep 18;23(52):12690-12703. doi: 10.1002/chem.201702117. Epub 2017 Jul 27. Chemistry. 2017. PMID: 28590540 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA-Encoded Macrocyclic Peptide Library.Methods Mol Biol. 2019;2001:273-284. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-9504-2_12. Methods Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 31134575
-
Targeting intracellular protein-protein interactions with cell-permeable cyclic peptides.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2017 Jun;38:80-86. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2017.03.011. Epub 2017 Apr 4. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2017. PMID: 28388463 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative Analysis of Cyclization Techniques in Stapled Peptides: Structural Insights into Protein-Protein Interactions in a SARS-CoV-2 Spike RBD/hACE2 Model System.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 21;25(1):166. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010166. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38203338 Free PMC article.
-
DLiP-PPI library: An integrated chemical database of small-to-medium-sized molecules targeting protein-protein interactions.Front Chem. 2023 Jan 9;10:1090643. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2022.1090643. eCollection 2022. Front Chem. 2023. PMID: 36700083 Free PMC article.
-
Marine Cyclic Peptides: Antimicrobial Activity and Synthetic Strategies.Mar Drugs. 2022 Jun 15;20(6):397. doi: 10.3390/md20060397. Mar Drugs. 2022. PMID: 35736200 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibitors of protein-protein interactions (PPIs): an analysis of scaffold choices and buried surface area.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2018 Jun;44:75-86. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2018.06.004. Epub 2018 Jun 13. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2018. PMID: 29908451 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting Ras with Macromolecules.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2018 Mar 1;8(3):a031476. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a031476. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2018. PMID: 28778966 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

