Considerable knock-on displacement of metal atoms under a low energy electron beam
- PMID: 28298631
- PMCID: PMC5428036
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-00251-3
Considerable knock-on displacement of metal atoms under a low energy electron beam
Abstract
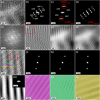
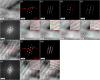
Under electron beam irradiation, knock-on atomic displacement is commonly thought to occur only when the incident electron energy is above the incident-energy threshold of the material in question. However, we report that when exposed to intense electrons at room temperature at a low incident energy of 30 keV, which is far below the theoretically predicted incident-energy threshold of zirconium, Zircaloy-4 (Zr-1.50Sn-0.25Fe-0.15Cr (wt.%)) surfaces can undergo considerable displacement damage. We demonstrate that electron beam irradiation of the bulk Zircaloy-4 surface resulted in a striking radiation effect that nanoscale precipitates within the surface layer gradually emerged and became clearly visible with increasing the irradiation time. Our transmission electron microscope (TEM) observations further reveal that electron beam irradiation of the thin-film Zircaly-4 surface caused the sputtering of surface α-Zr atoms, the nanoscale atomic restructuring in the α-Zr matrix, and the amorphization of precipitates. These results are the first direct evidences suggesting that displacement of metal atoms can be induced by a low incident electron energy below threshold. The presented way to irradiate may be extended to other materials aiming at producing appealing properties for applications in fields of nanotechnology, surface technology, and others.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Was, G. S. Fundamentals of radiation materials science: metals and alloys (Springer, New York, 2007).
-
- Murty, K. L., Charit, I. An introduction to nuclear materials: fundamentals and applications (Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2013).
-
- Hren, J. J., Goldstein, J. I. & Joy, D. C. Introduction to analytical electron microscopy (Springer, New York, 1979).
-
- Williams, D. B. & Carter C. B. Transmission electron microscopy: a textbook for materials science (Springer, New York, 2009).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

