Application of Micropore Filter Technology: Exploring the Blood Flow Path in Arterial-Line Filters and Its Effect on Bubble Trapping Functions
- PMID: 28298665
- PMCID: PMC5347218
Application of Micropore Filter Technology: Exploring the Blood Flow Path in Arterial-Line Filters and Its Effect on Bubble Trapping Functions
Abstract
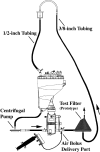
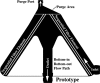
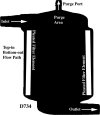
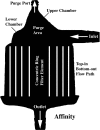
Conventional arterial-line filters commonly use a large volume circular shaped housing, a wetted micropore screen, and a purge port to trap, separate, and remove gas bubbles from extracorporeal blood flow. Focusing on the bubble trapping function, this work attempts to explore how the filter housing shape and its resulting blood flow path affect the clinical application of arterial-line filters in terms of gross air handling. A video camera was used in a wet-lab setting to record observations made during gross air-bolus injections in three different radially designed filters using a 30-70% glycerol-saline mixture flowing at 4.5 L/min. Two of the filters both had inlet ports attached near the filter-housing top with bottom oriented outlet ports at the bottom, whereas the third filter had its inlet and outlet ports both located at the bottom of the filter housing. The two filters with top-in bottom-out fluid paths were shown to direct the incoming flow downward as it passed through the filter, placing the forces of buoyancy and viscous drag in opposition to each other. This contrasted with the third filter's bottom-in bottom-out fluid path, which was shown to direct the incoming flow upward so that the forces of buoyancy and viscous drag work together. The direction of the blood flow path through a filter may be important to the application of arterial-line filter technology as it helps determine how the forces of buoyancy and flow are aligned with one another.
Keywords: application; arterial-line; cardio-pulmonary bypass equipment; filtration; micro-bubble; micropore; patient safety; radial.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
