Comparison of Oral Clonidine, Oral Dexmedetomidine, and Oral Midazolam for Premedication in Pediatric Patients Undergoing Elective Surgery
- PMID: 28298782
- PMCID: PMC5341645
- DOI: 10.4103/0259-1162.194586
Comparison of Oral Clonidine, Oral Dexmedetomidine, and Oral Midazolam for Premedication in Pediatric Patients Undergoing Elective Surgery
Abstract
Background: Midazolam has been commonly used orally for premedication in children. A search for a better alternative continues to overcome its side effects. Recently alpha-2 agonists, clonidine, and dexmedetomidine have been used for premedication in children.
Aim: To study and compare the efficacy of oral clonidine, oral dexmedetomidine, and oral midazolam for premedication in pediatric surgical patients.
Settings and design: This prospective, randomized, double blind study was conducted in a tertiary care hospital.
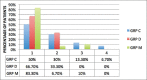
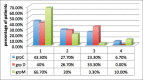
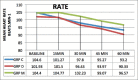
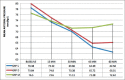
Materials and methods: The study was conducted in ninety children of either sex, in the age group of 4-12 years and the American Society of Anesthesiologists Physical status I, posted for ophthalmic surgery. Patients were randomly allocated to one of the three groups of thirty patients each: Group M: Oral midazolam 0.5 mg/kg body weight, Group D: Oral dexmedetomidine 4 μg/kg body weight, and Group C: Oral clonidine 4 μg/kg body weight. Patients were assessed for sedation, anxiolysis, and change in heart rate and blood pressure in the preoperative area. Behavior of children at separation from parents, mask acceptance, and side effects if any were noted. Statistical Analysis:: Data analysis was performed by unpaired Student's t-test and Chi-square test. Results:: Children in oral midazolam group achieved faster onset of sedation, higher sedation score, and lower anxiety score as compared to other two groups. The Group D and Group M were comparable as regards behavior at separation from parents (P = 0.236), but Group D was significantly better than Group C (P = 0.031). The three groups were comparable as regards providing satisfactory mask acceptance (P = 0.163). A number of children with easy separation from parents and excellent mask acceptance were significantly more in Group M as compared to Groups C and D (P = 0.028 and P = 0.012, respectively). Group C and Group D showed a lower mean arterial pressure at 45 min (P < 0.001) and 60 min after premedication (P < 0.001) as compared to Group M. Conclusion:: Oral midazolam is superior to the oral clonidine, and oral dexmedetomidine with faster onset of sedation, higher sedation score, lower anxiety score, and greater number of children with easy separation and excellent mask acceptance.
Keywords: Clonidine; dexmedetomidine; midazolam; pediatric; premedication.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A comparison of oral midazolam and oral dexmedetomidine as premedication in pediatric anesthesia.Saudi J Anaesth. 2016 Oct-Dec;10(4):390-394. doi: 10.4103/1658-354X.177333. Saudi J Anaesth. 2016. PMID: 27833480 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of intranasal dexmedetomidine and dexmedetomidine-ketamine for premedication in pediatrics patients: A randomized double-blind study.Anesth Essays Res. 2016 May-Aug;10(2):349-55. doi: 10.4103/0259-1162.172340. Anesth Essays Res. 2016. PMID: 27212773 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison between dexmedetomidine and midazolam premedication in pediatric patients undergoing ophthalmic day-care surgeries.Anesth Essays Res. 2013 May-Aug;7(2):248-56. doi: 10.4103/0259-1162.118982. Anesth Essays Res. 2013. PMID: 25885842 Free PMC article.
-
Oral Dexmedetomidine Achieves Superior Effects in Mitigating Emergence Agitation and Demonstrates Comparable Sedative Effects to Oral Midazolam for Pediatric Premedication: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Studies.J Clin Med. 2024 Feb 19;13(4):1174. doi: 10.3390/jcm13041174. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38398486 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of different sedatives in children before general anaesthesia for selective surgery: A network meta-analysis.J Clin Pharm Ther. 2022 Oct;47(10):1495-1505. doi: 10.1111/jcpt.13763. Epub 2022 Aug 27. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2022. PMID: 36029118 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison of oral dexmedetomidine and midazolam for premedication and emergence delirium in children after dental procedures under general anesthesia: a retrospective study.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018 Mar 28;12:647-653. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S163828. eCollection 2018. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018. PMID: 29636599 Free PMC article.
-
Paediatric preoperative sedation practices in tertiary maternity and children's hospitals in China: a questionnaire survey.BMC Pediatr. 2021 Aug 9;21(1):336. doi: 10.1186/s12887-021-02802-0. BMC Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 34372814 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Midazolam Oral Solution for Sedative Hypnosis and Anti-anxiety in Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Mar 18;11:225. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00225. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32256348 Free PMC article.
-
A comparative evaluation of dexmedetomidine and midazolam in pediatric sedation: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials with trial sequential analysis.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2020 Aug;26(8):862-875. doi: 10.1111/cns.13377. Epub 2020 Apr 29. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2020. PMID: 32347647 Free PMC article.
-
A Comparative Evaluation of Oral Clonidine, Dexmedetomidine, and Melatonin As Premedicants in Pediatric Patients Undergoing Subumbilical Surgeries.Rom J Anaesth Intensive Care. 2020 Jul;27(1):35-42. doi: 10.2478/rjaic-2020-0006. Epub 2020 Aug 10. Rom J Anaesth Intensive Care. 2020. PMID: 34056123 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Egan KJ, Ready LB, Nessly M, Greer BE. Self-administration of midazolam for postoperative anxiety: A double blinded study. Pain. 1992;49:3–8. - PubMed
-
- Feld LH, Negus JB, White PF. Oral midazolam preanesthetic medication in pediatric outpatients. Anesthesiology. 1990;73:831–4. - PubMed
-
- Gutstein HB, Johnson KL, Heard MB, Gregory GA. Oral ketamine preanesthetic medication in children. Anesthesiology. 1992;76:28–33. - PubMed
-
- Kain ZN, Hofstadter MB, Mayes LC, Krivutza DM, Alexander G, Wang SM, et al. Midazolam: Effects on amnesia and anxiety in children. Anesthesiology. 2000;93:676–84. - PubMed
-
- Bergendahl H, Lönnqvist PA, Eksborg S. Clonidine in paediatric anaesthesia: Review of the literature and comparison with benzodiazepines for premedication. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2006;50:135–43. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

