Effect of Periradial Administration of Papaverine on Radial Artery Diameter
- PMID: 28298790
- PMCID: PMC5341672
- DOI: 10.4103/0259-1162.194579
Effect of Periradial Administration of Papaverine on Radial Artery Diameter
Abstract
Background: Radial artery cannulation is a skillful procedure. An experienced anesthesiologist might also face difficulty in cannulating a feeble radial pulse.
Aim: The purpose of the study was to determine whether periradial subcutaneous administration of papaverine results in effective vasodilation and improvement in the palpability score of radial artery.
Settings and design: Prospective, double-blinded trial.
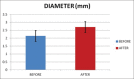
Methodology: Thirty patients undergoing elective cardiac surgery were enrolled in the study. 30 mg of papaverine with 1 ml of 2% lignocaine and 3 ml of normal saline were injected subcutaneously 1-2 cm proximal to styloid process of the radius. Radial artery diameter before and after 20 min of injection papaverine was measured using ultrasonography. The palpability of the radial pulse was also determined before the injection of papaverine and 20 min later. Patients were monitored for hemodynamics and any complications were noted.
Statistical analysis used: Student's t-test for paired data.
Results: Radial artery diameter increased significantly (P < 0.0001), and the pulse palpability score also showed statistically significant improvement (P < 0.0001) after periradial subcutaneous administration of papaverine. There was no statistically significant difference in heart rate, mean arterial blood pressure before and after papaverine injection. No complications were noted in 24 h of follow-up.
Conclusion: Periradial subcutaneous administration of papaverine significantly increased the radial artery diameter and pulse palpability score, which had an impact on ease of radial artery cannulation essential for hemodynamic monitoring in cardiac surgical patients.
Keywords: Papaverine; pulse palpability score; radial artery.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of subcutaneously infiltrated nitroglycerin on diameter, palpability, ease-of-puncture and pre-cannulation spasm of radial artery during transradial coronary angiography.Indian Heart J. 2014 Nov-Dec;66(6):593-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ihj.2014.05.023. Epub 2014 Jun 7. Indian Heart J. 2014. PMID: 25634390 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Facilitation of radial artery cannulation by periradial subcutaneous administration of nitroglycerin.J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2009 Sep;20(9):1151-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jvir.2009.05.034. Epub 2009 Jul 29. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2009. PMID: 19640734 Clinical Trial.
-
Subcutaneous Nitroglycerin for Radial Arterial Catheterization in Pediatric Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial.Anesthesiology. 2020 Jul;133(1):53-63. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000003308. Anesthesiology. 2020. PMID: 32282432 Clinical Trial.
-
Subcutaneous administration of nitroglycerin to facilitate radial artery cannulation.Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2006 Sep;68(3):389-91. doi: 10.1002/ccd.20881. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2006. PMID: 16892435
-
Radial artery cannulation: a comprehensive review of recent anatomic and physiologic investigations.Anesth Analg. 2009 Dec;109(6):1763-81. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0b013e3181bbd416. Anesth Analg. 2009. PMID: 19923502 Review.
Cited by
-
The effect of papaverine on tendon healing and adhesion in rats following Achilles tendon repair.Jt Dis Relat Surg. 2024 Apr 26;35(2):368-376. doi: 10.52312/jdrs.2024.1656. Epub 2024 Apr 26. Jt Dis Relat Surg. 2024. PMID: 38727117 Free PMC article.
-
Papaverine use for radial artery sheath entrapment.Anatol J Cardiol. 2019 Jun;22(1):44-45. doi: 10.14744/AnatolJCardiol.2019.71597. Anatol J Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 31264661 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Agostoni P, Biondi-Zoccai GG, de Benedictis ML, Rigattieri S, Turri M, Anselmi M, et al. Radial versus femoral approach for percutaneous coronary diagnostic and interventional procedures; Systematic overview and meta-analysis of randomized trials. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004;44:349–56. - PubMed
-
- He GW, Yang CQ. Radial artery has higher receptor-mediated contractility but similar endothelial function compared with mammary artery. Ann Thorac Surg. 1997;63:1346–52. - PubMed
-
- Ouadhour A, Sideris G, Smida W, Logeart D, Stratiev V, Henry P. Usefulness of subcutaneous nitrate for radial access. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2008;72:343–6. - PubMed
-
- Pancholy SB, Coppola J, Patel T. Subcutaneous administration of nitroglycerin to facilitate radial artery cannulation. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2006;68:389–91. - PubMed
-
- He GW, Yang CQ. Comparative study on calcium channel antagonists in the human radial artery: Clinical implications. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2000;119:94–100. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources