Efficacy and Safety of Modified Banxia Xiexin Decoction (Pinellia Decoction for Draining the Heart) for Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 28298938
- PMCID: PMC5337392
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/9591319
Efficacy and Safety of Modified Banxia Xiexin Decoction (Pinellia Decoction for Draining the Heart) for Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Modified Banxia Xiexin decoction (MBXD) is a classical Chinese herbal formula in treating gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) for long time, but the efficacy of it is still controversial. This study is to evaluate the efficacy and safety of MBXD for the treatment of GERD in adults. The search strategy was carried out for publications in seven electronic databases. RevMan software version 5.3 and the Cochrane Collaboration's risk of bias tool were performed for this review. Twelve RCTs were included for the analysis. The results of overall clinical efficacy and efficacy under gastroscope demonstrated that MBXD was superior to conventional western medicine. Meanwhile, the results of subgroup analysis showed clinical heterogeneity between the two groups. However, there was no statistically significant difference in acid regurgitation between the two groups. But in the improvement of heartburn and sternalgia, the results showed statistically significant differences for the comparison between two groups. In addition, the adverse reactions of the experiment groups were not different from those of the control groups. This systematic review indicates that MBXD may have potential effects on the treatment of patients with GERD. But because the evidence of methodological quality and sample sizes is weak, further standardized researches are required.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
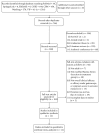











References
-
- Nocon M., Labenz J., Jaspersen D., et al. Health-related quality of life in patients with gastro-oesophageal reflux disease under routine care: 5-year follow-up results of the ProGERD study. Alimentary Pharmacology and Therapeutics. 2009;29(6):662–668. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2008.03921.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wahlqvist P., Karlsson M., Johnson D., Carlsson J., Bolge S. C., Wallander M.-A. Relationship between symptom load of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease and health-related quality of life, work productivity, resource utilization and concomitant diseases: survey of a US cohort. Alimentary Pharmacology and Therapeutics. 2008;27(10):960–970. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2008.03671.x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

