The effect of short polyethylene fiber with different weight percentages on diametral tensile strength of conventional and resin modified glass ionomer cements
- PMID: 28298993
- PMCID: PMC5347300
- DOI: 10.4317/jced.53550
The effect of short polyethylene fiber with different weight percentages on diametral tensile strength of conventional and resin modified glass ionomer cements
Abstract
Background: The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of polyethylene fiber on diametral tensile strength of conventional and resin modified glass ionomer cements.
Material and methods: 60 specimens in 6 groups (n=10) were prepared. In group 1 conventional glass ionomer (Fuji GC) and in group 2 resin modified glass ionomer (Fuji LC) were as control groups. In group 3 and 4 conventional glass ionomers mixed with short polyethylene fibers in proportion of 1 wt% and 3 wt%, respectively. In fifth and sixth groups, resin modified glass ionomer and short polyethylene fibers were mixed in 1 and 3% wt, respectively. Samples were prepared in a round brass mold (6.5×2.5 mm). After thermo-cycling, the diametral tensile strength of the specimens were tested and data were analyzed with ANOVA and post-hoc tests (p<0.05).
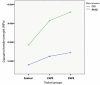
Results: Diametral tensile strength of both conventional and resin modified glass ionomer cements increased after mixing with polyethylene fiber (p<0.001). Also, reinforcement occurred as the mixing percentage increased from 1% wt to 3% wt in either conventional and resin modified glass ionomer (p<0.001).
Conclusions: The polyethylene fiber was shown to have a significant positive influence on diametral tensile strength of two types of glass ionomers. Key words:Conventional glass ionomer, diametral tensile strength, polyethylene fiber, resin modified glass ionomer.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement:The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exist.
Figures
References
-
- Paschoal MA, Gurgel CV, Rios D, Magalhães AC, Buzalaf MA, Machado MA. Fluoride release profile of a nanofilled resin-modified glass ionomer cement. Braz Dent J. 2011;22:275–9. - PubMed
-
- Hammouda IM. Reinforcement of conventional glass-ionomer restorative material with short glass fibers. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2009;2:73–81. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous