Conversion of lignin model compounds by Pseudomonas putida KT2440 and isolates from compost
- PMID: 28299400
- PMCID: PMC5486835
- DOI: 10.1007/s00253-017-8211-y
Conversion of lignin model compounds by Pseudomonas putida KT2440 and isolates from compost
Abstract
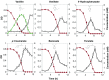
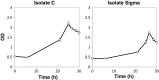
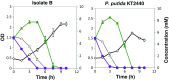
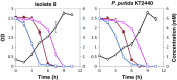
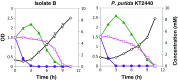
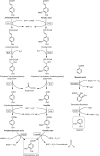
Starting from mature vegetable compost, four bacterial strains were selected using a lignin-rich medium. 16S ribosomal RNA identification of the isolates showed high score similarity with Pseudomonas spp. for three out of four isolates. Further characterization of growth on mixtures of six selected lignin model compounds (vanillin, vanillate, 4-hydroxybenzoate, p-coumarate, benzoate, and ferulate) was carried out with three of the Pseudomonas isolates and in addition with the strain Pseudomonas putida KT2440 from a culture collection. The specific growth rates on benzoate, p-coumarate, and 4-hydroxybenzoate were considerably higher (0.26-0.27 h-1) than those on ferulate and vanillate (0.21 and 0.22 h-1), as were the uptake rates. There was no direct growth of P. putida KT2440 on vanillin, but instead, vanillin was rapidly converted into vanillate at a rate of 4.87 mmol (gCDW h)-1 after which the accumulated vanillate was taken up. The growth curve reflected a diauxic growth when mixtures of the model compounds were used as carbon source. Vanillin, 4-hydroxybenzoate, and benzoate were preferentially consumed first, whereas ferulate was always the last substrate to be taken in. These results contribute to a better understanding of the aromatic metabolism of P. putida in terms of growth and uptake rates, which will be helpful for the utilization of these bacteria as cell factories for upgrading lignin-derived mixtures of aromatic molecules.
Keywords: Aromatic compound conversion; Bacterial metabolism; Compost; Lignin; Pseudomonas.
Conflict of interest statement
Funding
This work was financed by the Swedish Foundation for Strategic Research through the grant contract RBP14-0052.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Figures
References
-
- Ayyachamy M, Cliffe FE, Coyne JM, Collier J, Tuohy MG. Lignin: untapped biopolymers in biomass conversion technologies. Biomass Convers Biorefin. 2013;3(3):255–269. doi: 10.1007/s13399-013-0084-4. - DOI
-
- Belda E, van Heck RG, Lopez-Sanchez MJ, Cruveiller S, Barbe V, Fraser C, Klenk HP, Petersen J, Morgat A, Nikel PI, Vallenet D, Rouy Z, Sekowska A, Martins Dos Santos VA, de Lorenzo V, Danchin A, Médigue C. The revisited genome of Pseudomonas putida KT2440 enlightens its value as a robust metabolic chassis. Environ Microbiol. 2016;18(10):3403–3424. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.13230. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

